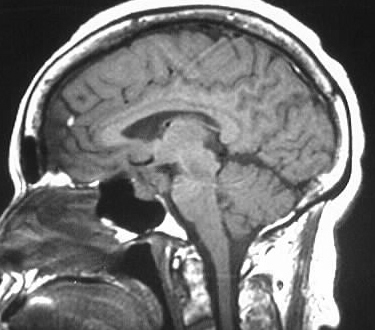
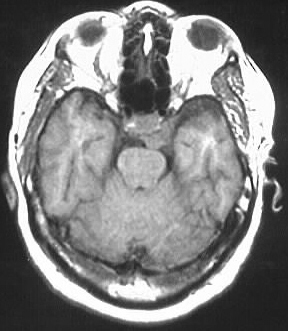
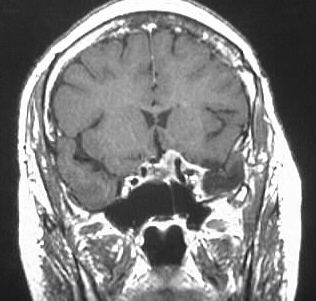
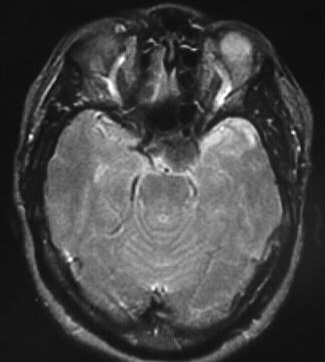
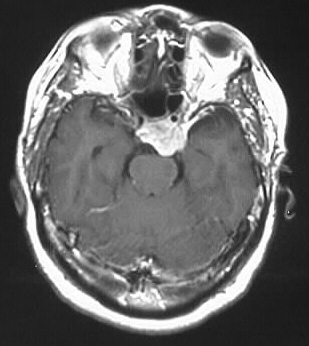
Meningioma
Findings:
Strongly enhancing cavernous sinus mass, hypo T2, iso
T1.
Differential Diagnosis:
meningioma, neuroma, pituitary adenoma, met, lymphoma,
aneurysm
Discussion:
distinguishing features: lens shaped/plaquelike appearance,
hypo T2
meningiomas typically hypo T2 due to fibrous content or
calcification, strongly enhance, iso noncon T1. broad dural base, extraaxial,
+/- dural tail. common locations convexity, interhemispheric, tent. Classically
iso to GM on all sequences.
-most common extraaxial neoplasm of adults
-15% of primary intracranial neoplasms,
peak 50-60, F 2:1 intracranial, 4:1 intraspinal
-25% of intraspinal neoplasms
-etiology unknown- ?trauma, radiation, virus,
familial
-origin=arachnoid cap cell, possible assn
with chr 22 deletion (9%- MISME)
-hormonally sensitive- pregnancy increases
size
-malignant/aggressive more common in peds
(imaging can't distinguish)
-globular or en plaque
-x ray: hyperostosis of inner table, enlarged
MMAs, Ca++, sinus expansion
-CT: hyperdense, variable edema (possibly
extensive), intense enhancement
-dural tail (60%)-nonspecific, +/-cysts,
+/- fat
-vascular supply: ECA 85%, ICA 63% -mother
in law sign- comes early, stays late
Grading WHO 1993
mening I
atypical mening II
papillary, HPC, anaplastic II-III