Sarcoidosis
Findings:
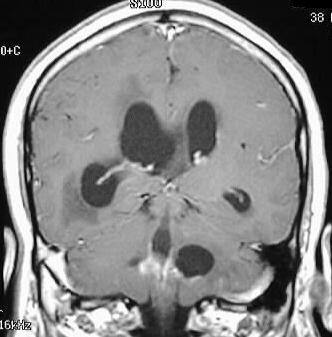
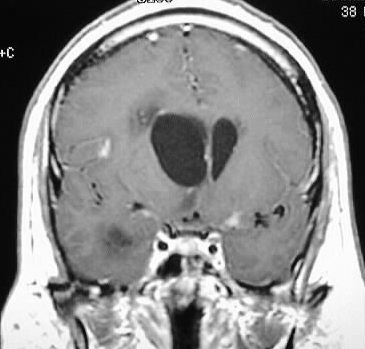
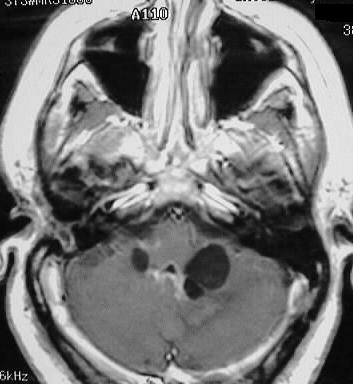
Coronal and axial postcontrast T1WI show asymmetric dilation
of the lateral ventricles, with mild R-L midline shift. The lateral fourth
ventricular foramina are markedly dilated and there is abnormal ependymal
enhancement in the fourth ventricle. Scattered small foci of abnormal leptomeningeal
enhancement are present.
Differential diagnosis:
Communicating hydrocephalus can be caused by any process
that impedes the normal resorptive function of arachnoid granulations,
ependyma, and lymphatics. Debris (SAH, infection, inflammation- sarcoid,
CP papilloma), cells (carcinomatosis), overproduction of CSF (CP papilloma),
or back-pressure (dural sinus or cortical vein thrombosis, NPH) can all
cause communicating hydrocephalus.
Discussion:
Hydrocephalus is the most common manifestation of
neurosarcoidosis.