Colloid Cyst
Findings:
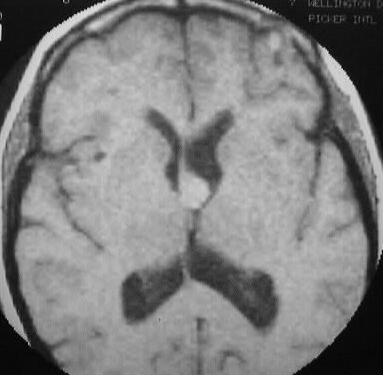
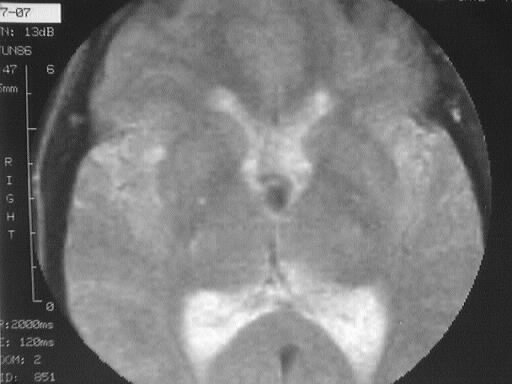
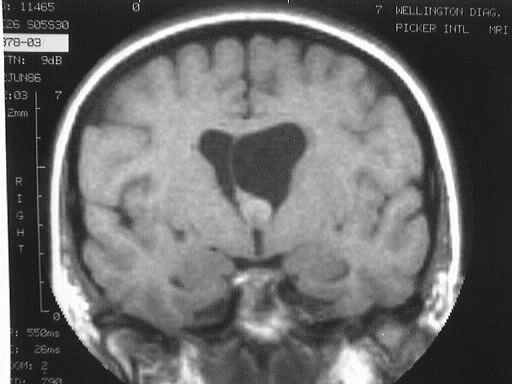
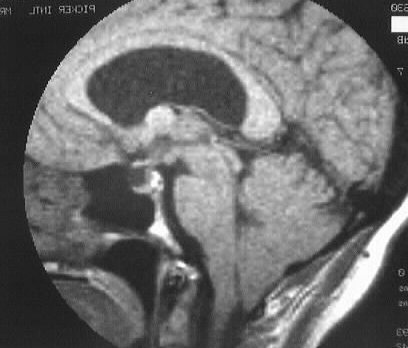
T1 and T2WI demonstrate a small mass in the region of
the left Foramen of Monro which is hyperintense on T1 and hypointense on
T2. Moderate ventricular asymmetry is present, consistent with obstructive
hydrocephalus.
Differential Diagnosis:
Few lesions other than colloid cyst exhibit these signal
characteristics, and probably shouldn't be considered. Other lesions in
this region include subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, central neurocytoma,
and subependymoma.
Discussion:
Colloid cyst comprises 1-3% of all intracranial tumors
and is almost always located in the anterior superior third ventricle.
It is the most common intraventricular neuroepithelial cyst, and is histologically
similar to a Rathke's cleft cyst. Clinically, the patient may present with
positional headaches. The lesion may obstruct the foramen of Monro acutely
and could cause sudden death. Imaging appearance is variable, with
most lesions hyperdense on CT, hyper T1/hypo T2. The lesions do not calcify.
40% show rim enhancement, with rare solid enhancement.