Shear Injuries
Findings:
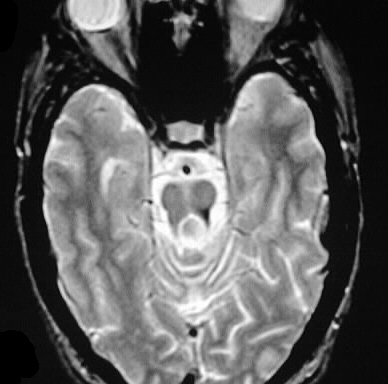
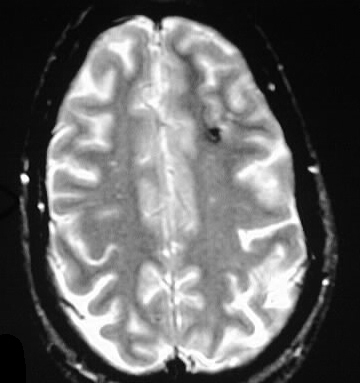
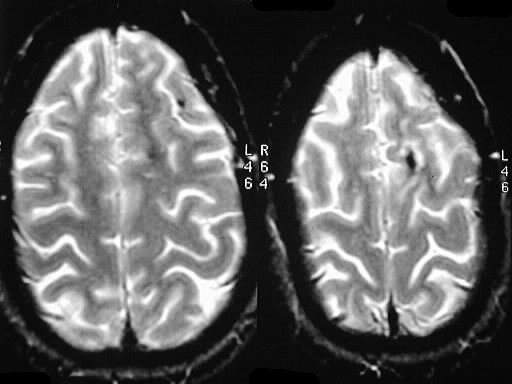
Axial GRE MR images demonstrate hypointensities compatible with hemorrhagic staining of the left superior cerebellar peduncle, left frontal subcortical white matter, and left frontal cortex.
Differential diagnosis:
shear injuries, remote microhemorrhages from hypertensive disease, treated hemorrhagic metastases, multiple cavernomas. The left SCP lesion is most characteristic for shear by location and morphology.
Discussion:
Diffuse axonal injury with or without hemorrhagic change is a common cause of morbidity in the setting of head trauma, and often results in long term disability. MR with T2* weighting is most sensitive for detection of shear injury. CT often underestimates the extent of DAI, but some shear injuries wil present as punctate hyperdensities in CT. Larger shear injuries, such as those involving the corpus callosum, will be visible on CT, as are many other manifestations of acute trauma. Without corresponding pertinent history, the differential diagnosis of small scattered hypointensities on T2* MR is quite broad.
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE


