Secondary CNS lymphoma in AIDS patient
Findings:
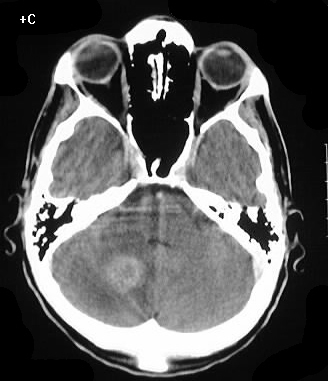
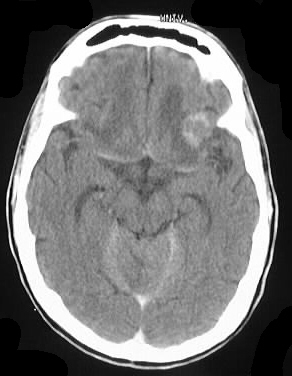
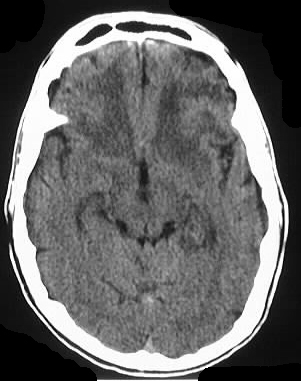
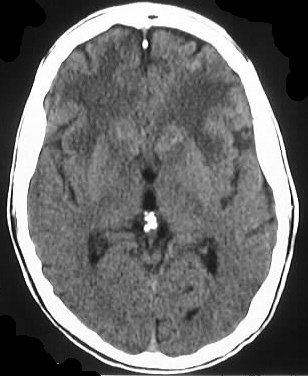
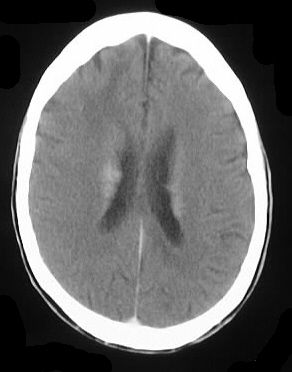
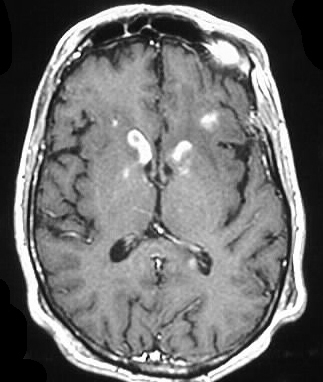
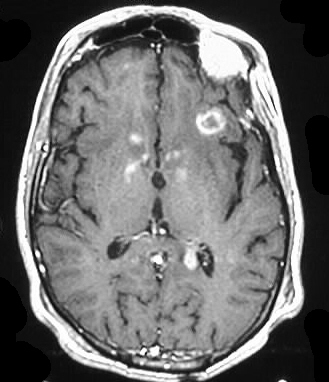
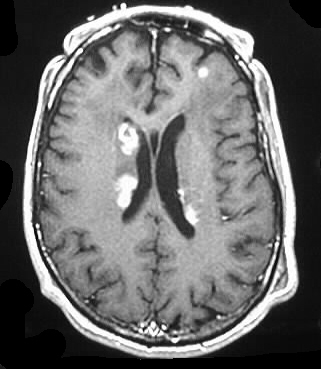
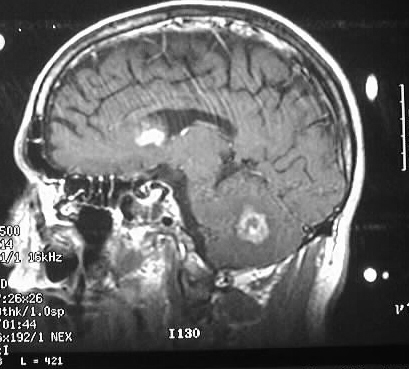
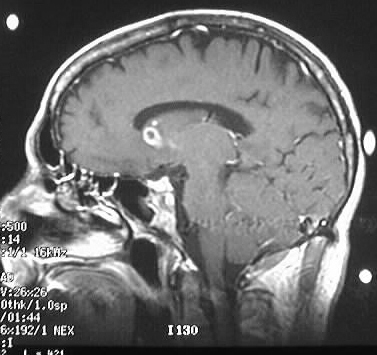
Axial noncontrast and contrast CT shows numerous enhancing
lesions throughout both cerebral hemispheres and a large lesion in the
right cerebellum, with surrounding edema and mass effect. The lesions show
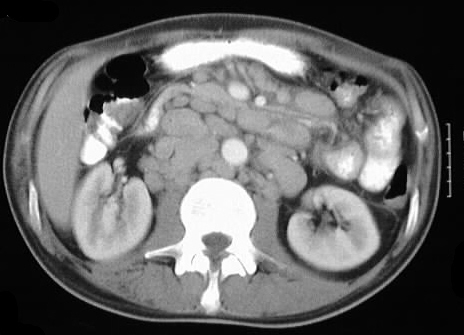
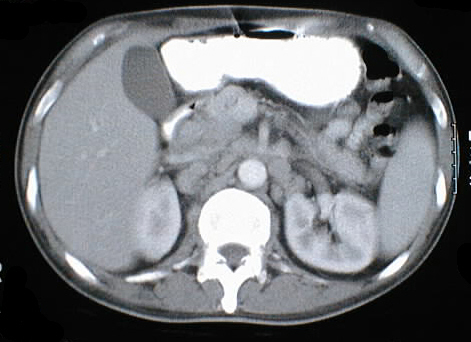
solid or ring enhancement on MR. Limited images from a CT of the abdomen
with contrast in the same patient shows diffuse adenopathy.
Differential Diagnosis:
Lymphoma and metastases would be the most likely
considerations. If findings were limited to the brain, toxoplasmosis could
also be considered, but it would still be uncommon to have a toxo lesion
this large in the cerebellum.
Discussion:
Secondary CNS lymphoma is usually high grade B-cell (Burkitt's
or immunoblastic), associated with a very poor prognosis (5 weeks average
survival). The lesions seen in AIDS are more commonly ring enhancing with
necrosis than those seen in immunocompetent individuals. Meningeal disease
is seen in 10-25%, which is not commonly seen in immunocompetent patients.
reference: Osborn, A.; Tong, K. Handbook of Neuroradiology: Brain and Skull. 2nd ed. 1996: Mosby Year Book. pp. 470-471.