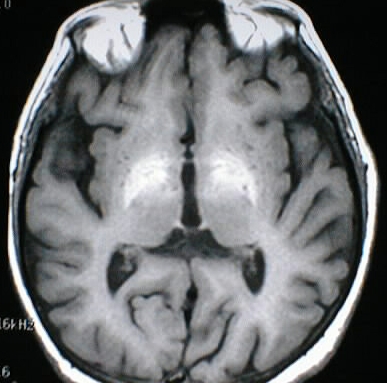
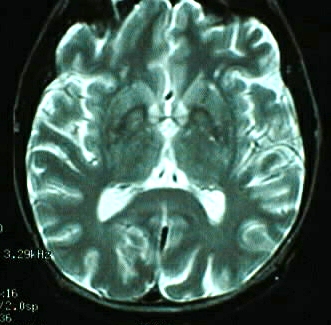
Liver Disease
Findings:
Axial T1 and T2 weighted images show symmetric abnormal
signal in the globus pallidus.
Differential Diagnosis/Discussion:
The differential diagnosis of symmetric abnormal signal
in the basal ganglia is broad, including metabolic etiologies (mitochondrial
disorders (Leigh), methylmalonic acidemia, Wilson's disease, Hallervorden-Spatz),
toxins (CO, methanol, cyanide), and hypoxic insult. Most of these disorders
cause nonspecific T1 hypointensity/T2 hyperintensity with the exception
of Hallervorden-Spatz. The pattern of symmetric T1 hyperintensity
may be seen with calcification, TPN, and liver disease.