Optic Neuritis- Multiple Sclerosis
Findings:
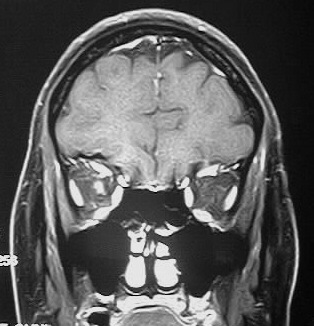
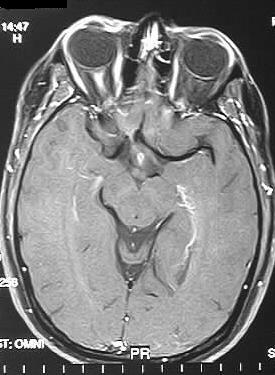
Coronal and axial fat suppressed postcontrast T1WI show
homogenous enhancement of the right optic nerve, without expansion. Axial
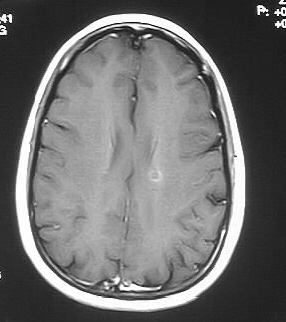
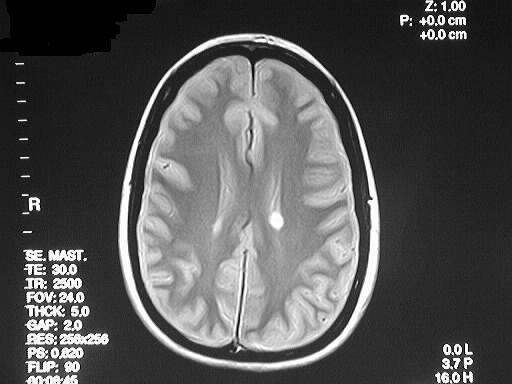
postcontrast T1 image demonstrates a small focus of faint enhancement
in the left centrum semiovale region. This lesion has marked hyperintensity
on the PD image.
Differential Diagnosis:
The differential diagnosis of optic nerve enhancement
includes optic neuritis due to MS, sarcoidosis, or ADEM. Mass lesions such
as optic glioma and meningioma probably shouldn't be considered since there
is no expansion of the optic nerve or nerve sheath.
Discussion:
MS is the most common primary demyelinating disorder,
affecting 1 in 1000 persons, 60% of which are female and 95% are age 18-50.
Other associations include myasthenia gravis, ulcerative colitis, and crohn's
disease. 70% have a waxing and waning course to distinguish from ADEM which
is monophasic.
Eponyms:
-Marburg dz- rapidly progressive course
with death in months
-Devic's dz- neuromyelitis optica-
visual system and spinal cord
-Balo's dz- concentric bands of demyelination
may simulate tumor but no mass effect
-Uthoff's phenomenon- symptoms worsened
by heat
-Dawson's fingers- characteristic
ovoid WM lesions perpendicular to vents
-50% of women with optic neuritis develop MS
-internuclear ophthalmoplegia most common oculomotor
finding in MS
(due to lesions
in periaqueductal grey)
-dual echo T2 most sensitive
-new lesions enhance, may be tumor-like
-70% of those with spinal MS have concurrent brain disease