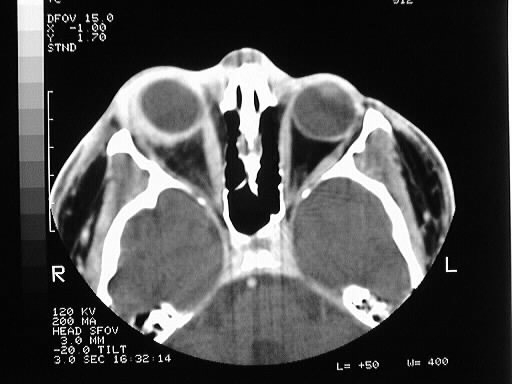
Findings:
Axial contrast CT of the orbits shows abnormal right
scleral thickening, assiciated with stranding in the orbital fat and mild
thickening of the extraocular muscle tendon attachments. The right medial
rectus muscle is slightly larger than the left.
Differential Diagnosis:
orbital pseudotumor, lymphoma, Grave's disease, less
likely metastatic disease
Discussion:
-orbital pseudotumor
-idiopathic nongranulomatous inflammatory
disorder
-third most common orbital disease (5%)
-children 15% of all cases
-acute onset with pain, swelling, erythema,
ptosis, painful/restricted eye movement
-acute form
usually responds to steroids
-uncommonly chronic with diplopia, proptosis
-chronic less
commonly responds to steroids- XRT or chemo may help
-involves lacrimal gland, EOMs, fat
-orbital apex, cavernous sinus= Tolosa Hunt-
painful ophthalmoplegia
-other systemic diseases associated:
-Wegener's,
PAN, RP fibrosis, PSC, Reidel's, SLE, RA, dermatomyositis
-imaging:
-tendons involved
and unilateral (to dist from Graves)
-marked enhancement
-retrobulbar
fat stranding
-may present
as focal or infiltrating mass
-rare bone
destruction
-T2 hypo to
dist from mets