Cholesterol Cyst
Findings:
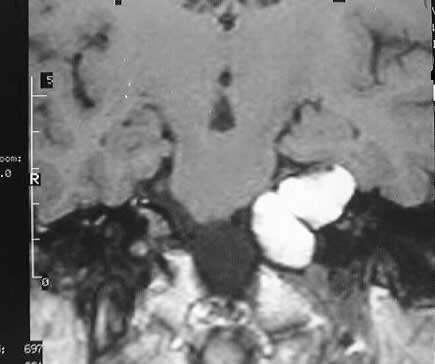
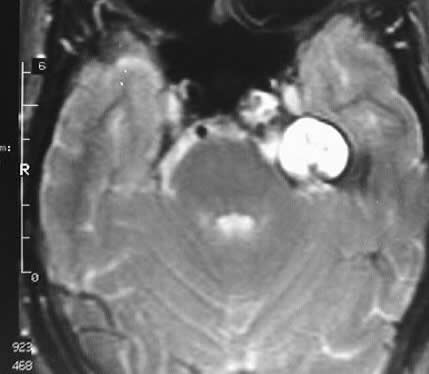
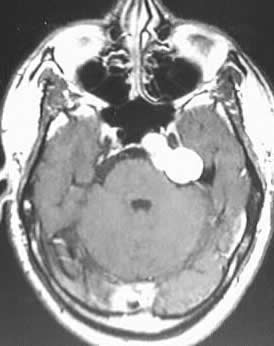
Multiple MR images show a lobulated expansile mass involving
the left petrous apex, which compresses the pons and extends into the prepontine
cistern. The mass demonstates homogenous hyperintensity on T1 and T2 weighted
images, and has no solid enhancing component.
Differential Diagnosis:
The signal characteristics are highly consistent with
a cholesterol granuloma or cyst, with lipoma or (epi)dermoid considered
much less likely. Other lesions to consider in this location with similar
signal characteristics include petrous apex mucocele, petrous apicitis,
and hemorrhagic metastasis. It is important to distinguish this lesion
from an epidermoid due to the difference in surgical approach.
Discussion:
Cholesterol cyst represents a foreign body reaction to
a small blood vessel rupture in the petrous bone. The small vessel rupture
may be caused by chronic negative pressure within the apex air cells due
to chronic middle ear obstruction. There is deposition of cholesterol crystals
and blood products by the petrous air cells, which gives the lesion a characteristic
signal profile. The lesions may cause symptoms referable to cranial nerves
V and VIII.
reference: Grossman, R; Yousem, D. Neuroradiology: the Requisites. 1994:Mosby
Year Book. p. 353.