Carotid Body Tumor (Paraganglioma)
Findings:
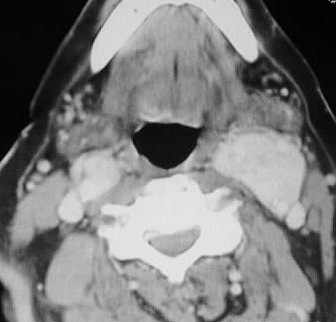
Axial contrast CT shows a strongly enhancing mass at
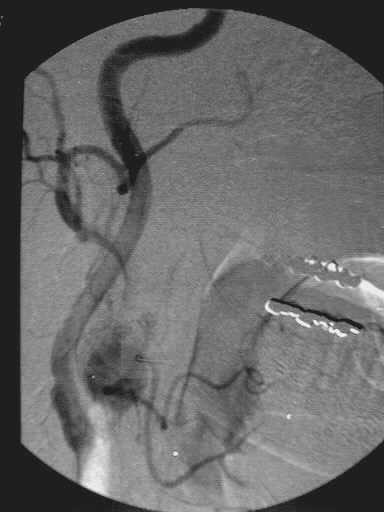
the level of the left carotid bifurcation. Oblique left common carotid
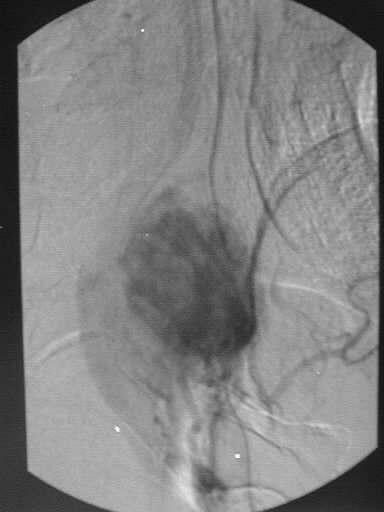
srteriogram demonstrates hypervascularity and prolonged vascular staining
of the mass.
Differential Diagnosis:
carotid body tumor, less likely hypervascular lymph node
metastasis
Discussion:
The normal carotid body regulates respiratory rate, tidal
volume, and sympathetic tone in response to hypoxia, hypercapnia, and acidosis.
Carotid body tumors are paragangliomas in the same family as glomus tumors
and pheochromocytomas, and are of neural crest origin. The tumors are markedly
hypervascular, with early and prolonged vascular staining on angiography.
MR characteristics include a "salt and pepper" appearance with numerous
flow voids, and are bilateral in 5%. The tumors have a 10% recurrence rate
after resection. Carotid body tumors uncommonly (5%) undergo malignant
transformation, with metastases.