Laryngopyocele
Findings:
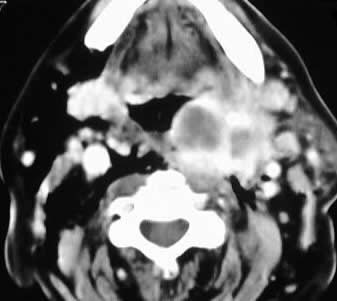
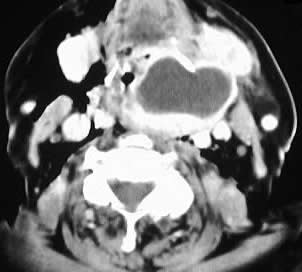
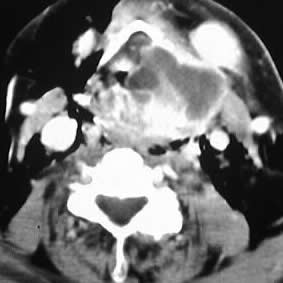
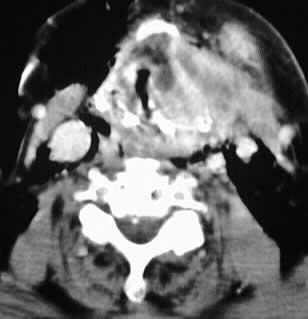
Axial contrast CT images of the neck show a fluid collection
with enhancing rim which originates at the level of the left laryngeal
ventricle, with marked narrowing of the airway and extent to the level
of the tongue base.
Differential Diagnosis:
laryngocele, laryngopyocele, necrotic supraglottic tumor.
Discussion:
A laryngocele represents an abnormally dilated appendix
of the laryngeal ventricle. The lesion is caused by chronically elevated
intraglottic pressure as may be seen in trumpet players and other musicians.
Other predisposing situations include glass blowers and chronic inflammatory
disease. Those who develop a laryngocele without a known predisposing factor
should be investigated for a tumor causing obstruction of the laryngeal
ventricle. The lesions may be air or fluid filled, and may become infected
as in this case. External and internal laryngoceles are distinguished by
penetration through the thyrohyoid membrane, although the mixed type is
most common.