Giant Petrous/Cavernous ICA Aneurysm
Findings:
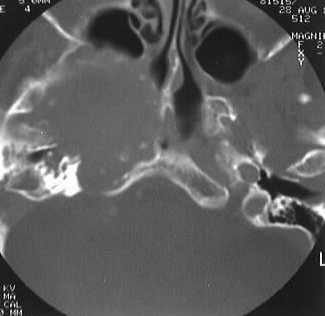
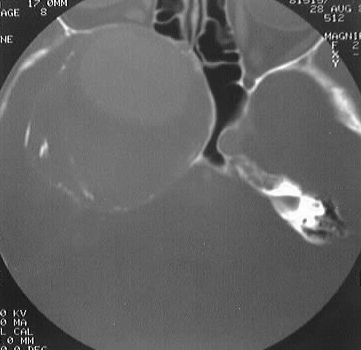
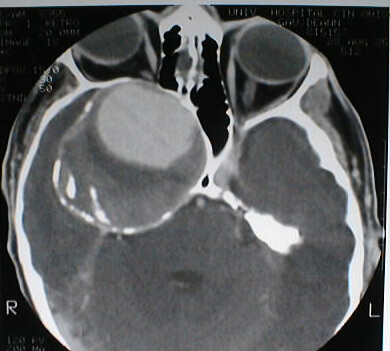
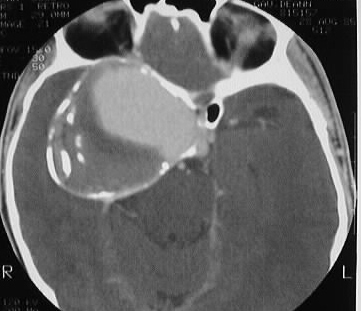
Axial contrast CT with bone windows shows a large expansile
lesion with rim calcification in the region of the right parasellar ICA,
associated with marked bone remodeling and effacement of the right sphenoid
and ethmoid sinuses. A large area of vascular enhancement is present centrally
within the lesion, with thrombus in the peripheral areas.
Discussion:
A giant aneurysm is defined as an intracranial aneurysm
greater than 2.5 cm in diameter, and accounts for approximately 5 percent
of the total. These types of aneurysms are relatively more common in children
and young adults, with greater than 50 percent arising from the posterior
circulation. Conventional angiography, as in peripheral angiographic evaluation
of AAA, can grossly underestimate the size of these lesions due to mural
thrombus. Size is best evaluated with CT or MR.