Sturge-Weber Syndrome
Findings:
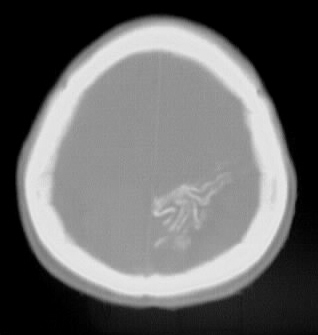
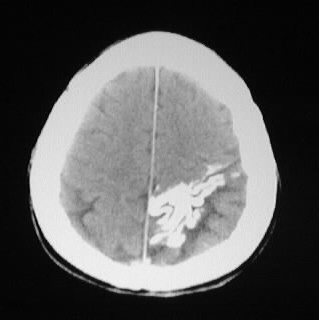
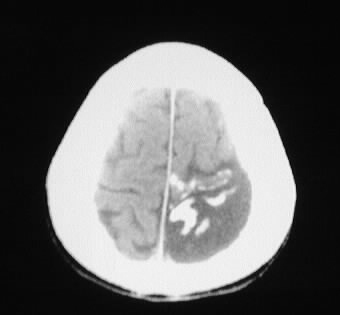
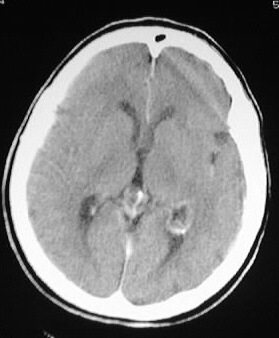
Multiple CT images show left parietooccipital gyral calcification,
associated with focal cortical atrophy and enlargement of the ipsilateral
choroid plexus.
Differential Diagnosis:
Sturge Weber syndrome, calcified infarct, celiac disease
with folate deficiency
Discussion:
Sturge Weber syndrome is a rare angiomatous process of
unknown inheritance that is included with the neurocutaneous syndromes.
The syndrome is possibly related to persistent primordial sinusoidal vascular
supply.
-clinical:
-sz 90%
-hemiplegia 30%
-40-90% mental decline<2 years
-glaucoma 30%
-port wine stain in V1 distribution
-variants- facial/intracranial without eye, etc.
I= facial nevus + pial angioma
II= facial nevus
III= pial angioma
-trigeminal dermatome- all 3>>1+2>>other
-eye manifestations (33%):
-bupthalmos-large globe
-congenital glaucoma
-choroidal angioma
-episcleral telangiectasia
-angiomas of EOM
-also assd with Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome
-intracranial:
-pial angioma with calcification,
paucity of cortical veins, retrograde drainage to medullary veins
-enlarged choroid plexus
-most facial nevi overlie affected
brain
-chronic cerebral ischemia underlying
pial angioma,
-progressive cerebral calcification
(unusual <2yrs)
-may have cerebral hemiatrophy with
calvarial thickening and enlarged sinuses
-most common in parietooccipital