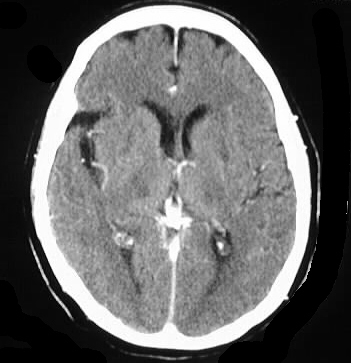
Extrapontine Myelinolysis
Findings:
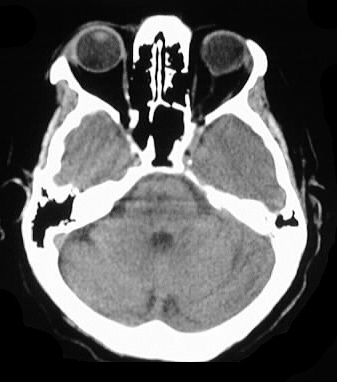
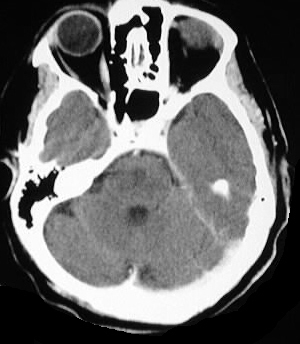
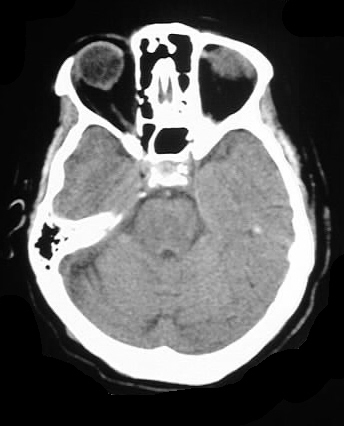
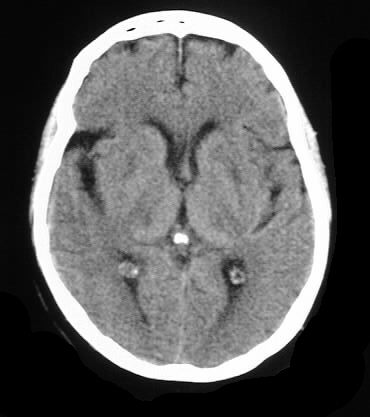
Axial CT images with and without contrast demonstrate
patchy areas of symmetric low attenuation in the pons, thalami, and basal
ganglia, without enhancement.
Differential Diagnosis:
central pontine/extrapontine myelinolysis, ADEM, MS less
likely
Discussion:
Central pontine myelinolysis occurs infrequently when
electrolyte disorders are corrected too quickly, and manifests clinically
as spastic paraparesis, pseudobulbar palsy, or "locked in" syndrome. While
the majority of cases are caused by rapid correction of hyponatremia or
associated with alcoholism, a variety of electrolyte and metabolic disorders
may have a role in CPM. Characteristic imaging features include symmetric
hypodensity or signal abnormality in the pontine transverse fibers. These
attenuation abnormalities can extend into the deep gray structures in up
to 50%.