
Plexiform Neurofibroma (NF1)
Findings:
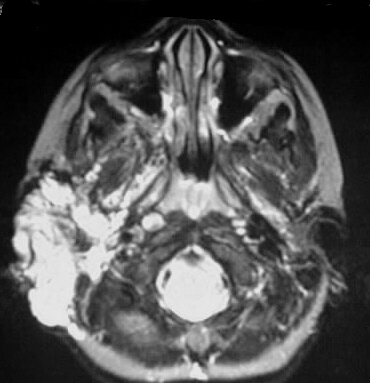
An infiltrative, mildly expansile mass is evident in
the right pre- and postauricular soft tissues. The mass has predominantly
high signal characteristics on T2WI and heterogenous isointensity to gray
matter on T1WI. The axial T2WI shows high signal foci in the basal ganglia
with extension to the internal capsule. An additional small hyperintensity
is seen in the left thalamus.
Differential Diagnosis:
The combination of basal ganglia T1 bright spots and
infiltrating superficial soft tissue lesion should lead to the diagnosis
of NF1. No other reasonable differential exists.
Discussion:
Neurofibromatosis type I- AD, 1/2500, 50% spontaneous
mutation
-clinical dx: 2 or more
-cafe au lait
spots (6 or more, >5mm child, >15 mm adult),
-NFs 2 or
more
-plexiform
NF
-axillary/intertriginous
freckles
-optic glioma
-lisch nodules
-bone lesions
-relative
with NF
-up to 50% of optic nerve gliomas assd with NF1
-cutaneous lesions
-cafe au lait
spots (coast of California, McCune Albright coast of Maine)
-freckling
intertriginous
-NFs, (TNTC
NFs=fibroma molluscum)
-elephantiasis
neuromatosa
-bone findings
-macrocephaly,
lambdoid defect, enlarged neural foramina (with or without NFs)
-sphenoid
dysplasia
-posterior
vertebral scalloping and scoliosis
-pseudarthrosis
-genu valgum/varum
-ribbon ribs
-tumors
-ONG
-cord astrocytomas
-malignant
peripheral nerve sheath tumors
-embryonal
tumors, leukemia, melanoma, medullary thyroid cancer
-other CNS lesions
-T1 bright
spots in GP ?etiology and significance
-cerebellar
hamartomas
-arachnoid
cyst, meningocele
-vascular lesions
-renal artery
stenosis
-smoothly
tapered stenosis/occlusion of visceral arteries
-coarctation
-intracranial
stenosis