Cortical Laminar Necrosis
Findings:
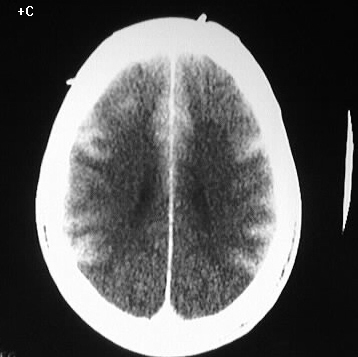
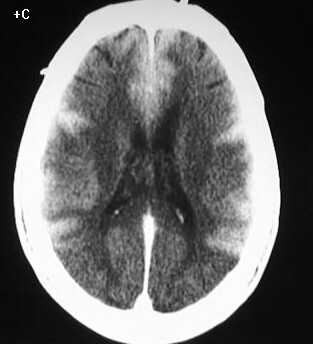
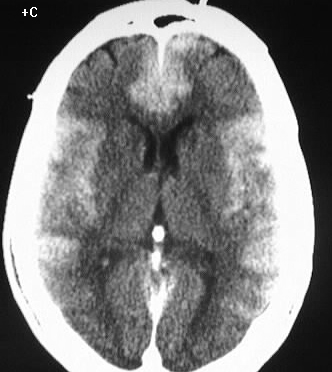
Axial contrast enhanced CT images show symmetric, thick,
abnormal enhancement of the cerebral cortex. White matter attenuation is
abnormally low, with loss of gray-white differentiation in the parietooccipital
regions. There is no definite mass effect.
Differential Diagnosis:
The appearance is characteristic for laminar necrosis
and no other reasonable differential diagnosis exists.
Discussion:
Laminar necrosis is a rare manifestation of neuronal
injury, with a very poor prognosis. The process results from oxygen and/or
glucose depletion as is seen with anoxia, hypoglycemia, status epilepticus,
or ischemic stroke. This marked cortical enhancement likely reflects a
diffuse loss of the blood brain barrier and cellular disruption. Focal
areas of laminar necrosis may be seen with arterial distribution infarctions,
and the MR appearance of these are well described in the literature.