Chiari II Malformation
Findings:
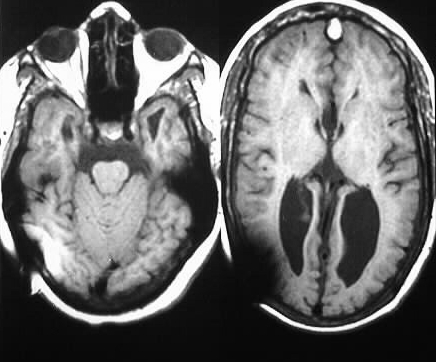
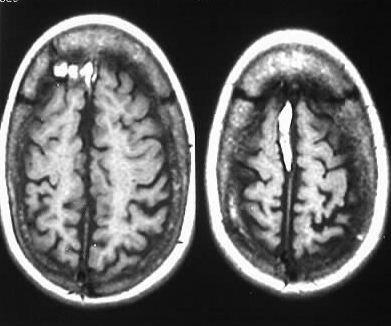
The axial MR images show colpocephaly and a towering
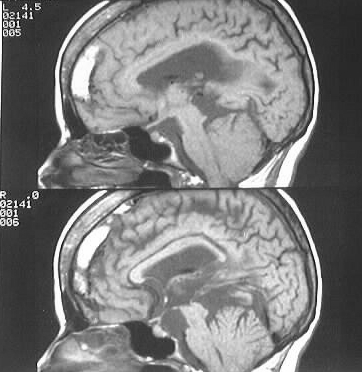
cerebellum extending through a widened tentorial hiatus. The sagittal images
show a small posterior fossa, associated with flattening and elongation
of the fourth ventricle. The tectum is pointed.
Discussion:
This constellation of findings is characteristic of Chiari
II malformation. Chiari II malformation is a relatively common congenital
CNS anomaly which represents an abnormality of neural tube closure at aproximately
4 weeks of gestation. The most common anomaly due to defective neural tube
closure is anencephaly. The basic abnormality in Chiari II malformation
is inadequate developmant of the fourth ventricle with a resultant small
posterior fossa. The associated findings are largely due to the small posterior
fossa. Myelomeningocele is almost universally present with this anomaly.
The condition can be hereditary and familial. Chiari II is in no way related
to Chiari I.
Associated intracranial findings (variable and rarely
all present):
-hydrocephalus, narrow aqueduct, large
foramen magnum
-lacunar skull- inner table scalloping-
resolves
-scalloped posterior petrous/clivus
-low tent, wide hiatus
-hypoplastic falx with gyral interdigitation
-vertical straight sinus
-lateral vents parallel with colpocephaly
and squaring of frontal horns
-80% absent septum pellucidum
-hourglass 3rd vent with large massa
intermedia
-long, low and small 4th vent
-beaked tectum with large QP cistern
-large caudate heads
-towering cerebellum
Extracranial findings:
->99% with myelomeningocele
-70% with deficient C1 posterior arch
-restrictive dural band at craniocervical
junction
-20% with diastematomyelia (20%)
-50% hydromyelia
-thoracolumbar kyphosis