Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Findings:
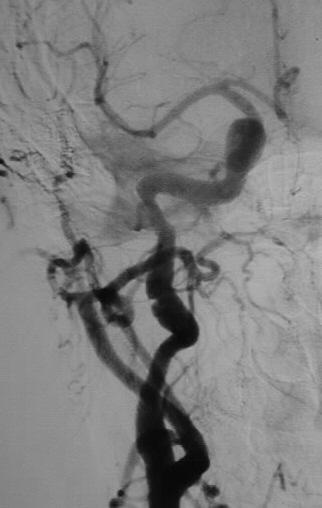
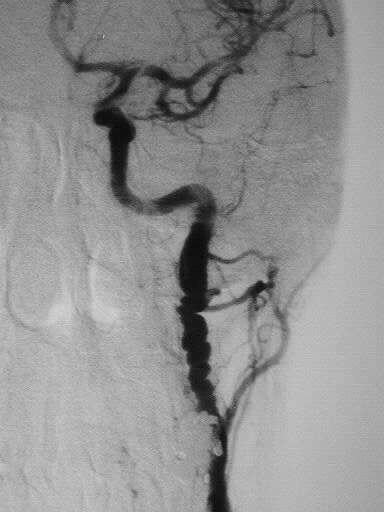
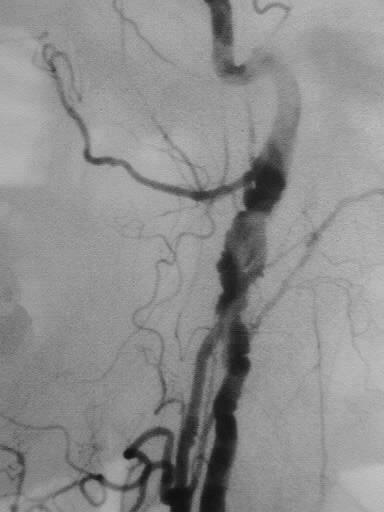
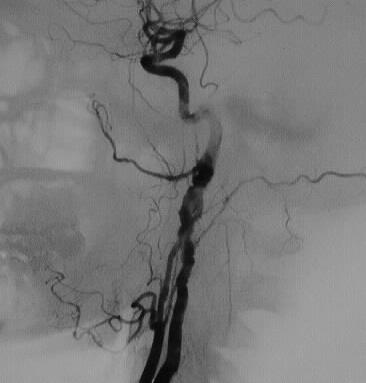
Bilateral common carotid arteriograms show irregular
beaded stenoses of the internal carotid arteries. The external carotid
arteries show minimal irregularity as well.
Differential Diagnosis:
The appearance is fairly characteristic for fibromuscular
dysplasia. Atherosclerotic disease would be more common overall, but the
location of disease would be atypical.
Discussion:
Fibromuscular dysplasia most commonly involves the renal
arteries of middle aged females, and represents an idiopathic proliferation
of the intima and/or media. Subtypes of this disease include intimal hyperplasia,
medial fibroplasia, fibromuscular hyperplasia, and subadventitial fibroplasia,
of which medial fibroplasia is the most common. The medial fibroplasia
type causes the typical "string of beads" appearance. 3% of cases involve
the internal carotids between the middle and distal thirds, with a 25%
incidence of intracranial aneurysms in these patients. Embolic strokes
may be seen as well. The vertebral arteries may also be involved, but this
is less common. Bilateral involvement is common.