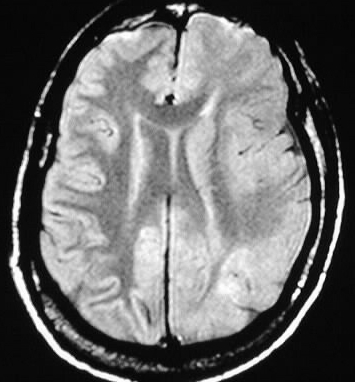
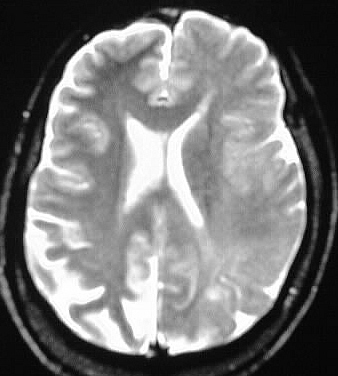
Hemimegalencephaly
Findings:
The left cerebral hemisphere is enlarged, associated
with asymmetry of the lateral ventricles. Gray-white differentiation is
indistinct and overall signal is increased in the left cerebral hemisphere,
with relative lack of sulcation in the left parietal region. Generalized
atrophy is present on the right.
Differential Diagnosis:
The appearance is characteristic for hemimegalencephaly.
A diffuse glioma could have a similar appearance, but a higher signal intensity
would be expected, and the abnormal sulcation would be unexplained.
Discussion:
Hemimegalencephaly represents a diffuse migrational anomaly
involving an entire cerebral hemisphere. The parenchyma is disorganized,
with hamartomatous proliferation, white matter abnormalities, and heterotopic
gray matter. The cortex may be calcified and dysplastic. Patients with
this anomaly typically have intractible seizures, and may require hemispherectomy.