Fibrous dysplasia
nFindings
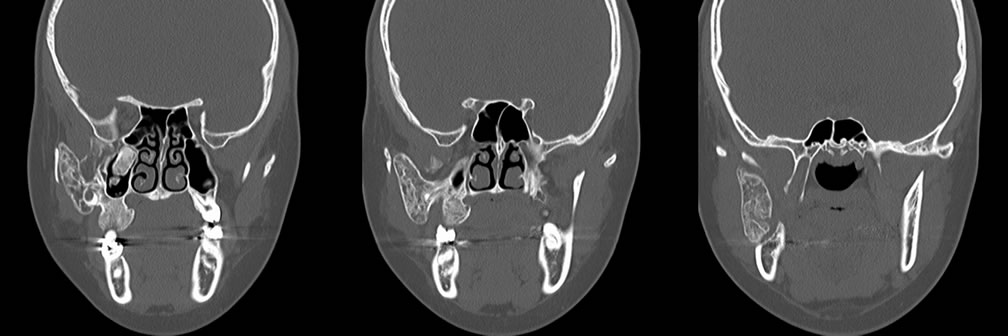
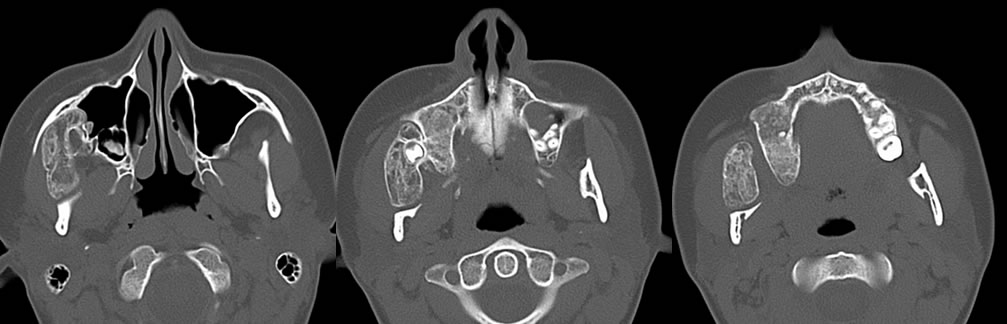
nAxial and coronal CT images display an expansile fibro-osseous lesion extending from and expanding the right maxilla. The lesion demonstrates ground glass appearance. The lesion extends superiorly deep to the right zygomatic arch and inferiorly along the angle of the right mandible with bony remodeling of the mandible.
nDifferential Diagnosis
nFibrous dysplasia, Paget disease, cemento-ossifying fibroma, primary or metastatic neoplasm
nDiscussion
nFibrous dysplasia is a congenital disorder of osteoblast dysfunction characterized by expanding lesions with a mixture of woven bone and fibrous tissue. The best diagnostic clue is a ground glass matrix in an expansile bone lesion. The majority of these lesions involve more than one bone, and typical patterns include involvement of maxilla, orbit, and frontal bone or ethmoids and sphenoids. Local bone remodeling is also seen with these lesions, however it does not tend to be quite as destructive as seen with malignancy. These are typically benign lesions, but may rarely progress to malignancy in 0.5% of cases.
Case contributed by Christopher Heald, UC M4
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE



