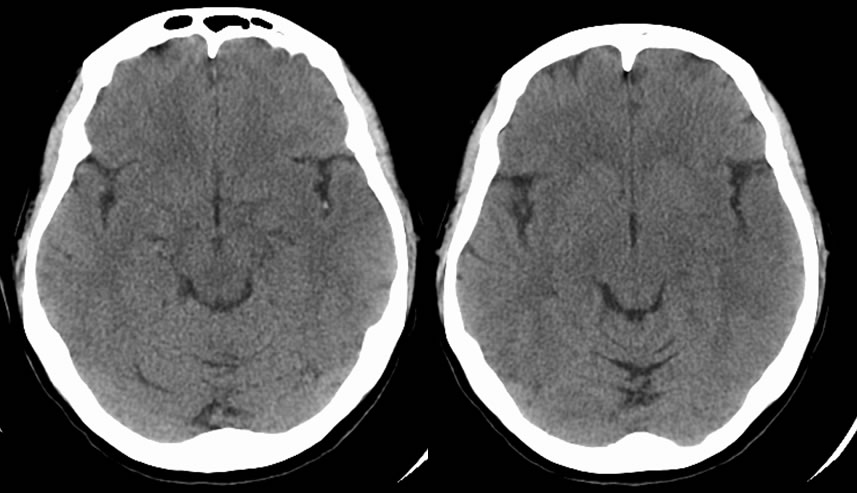
MCA Infarction- Dot Sign
Findings:
Axial CT images demonstrate a hyperdenisty in the left M2 branch of the middle cerebral artery. There is also loss of the left insular ribbon and asymmetric low attenuation within the left frontotemporal operculum.
Discussion:
Evaluation of acute infarction can be difficult on CT due to lack of sensitive imaging findings. In the hyperacute period, there are typically no changes in brain attenuation. A specific, but not sensitive, sign is a hyperdense vessel, which signifies thrombosis. The images above demonstrate a hyperdense M2 branch of the middle cerebral artery that has been imaged in cross-section. This is called the 'Dot Sign' because the vessel to appears as a bright "dot" within the Sylvian fissure. Another sign of MCA infarct in the acute period is the loss of the insular ribbon. The insular ribbon refers to the gray-white junction along the lateral portion of the insular cortex. Cytotoxic edema causes hypoattenuation of this area. As the infarct ages, other signs may appear including sulcal effacement. Ultimately, the infarcted area will appear as parenchymal hypodensity.
Case contributed by Christopher Heald, UC M4
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE

