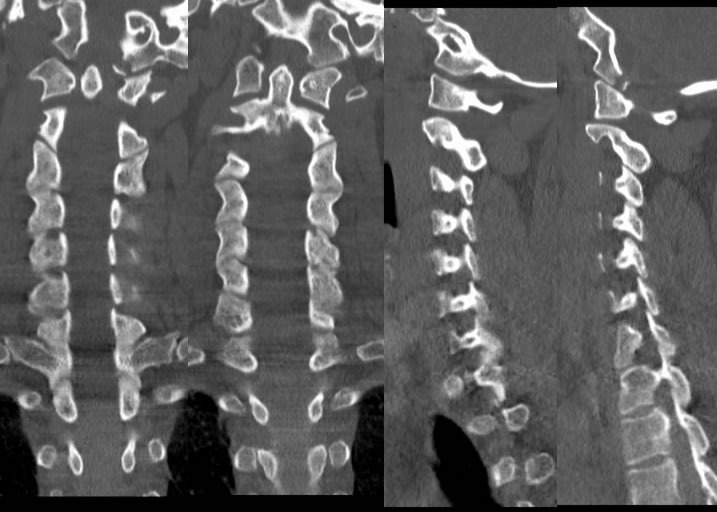
Left Occipital Condyle Fracture with widened right AO articulation
Findings:
Coronal and sagittal CT MPR demonstrates an avulsion fracture along the medial margin of the left occipital condyle, asssociated with asymmetric widening of the right atlantoocciptal joint. There is also relative subtle widening of the atlantoaxial joints.
Discussion:
Occipital condyle fractures are most common along the medial margin related to an axial loading and rotational force. The fractures are often difficult to see on axial images unless a high index of suspicion is used, but are frequently better visualized on coronal MPR. The fractures may be more complex and extend further into the skull base with a more devastating mechanism of high impact, as a component of more complex skull base fractures which may extend into the clivus, temporal bones, and/or carotid canals. These fractures may also be associated with craniocervical ligamentous injury, therefore craniocervical and atlantoaxial alignment must be carefully inspected for widened joints and/or other asymmetries.
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE

