


Bilateral vertebral artery dissection
Findings:
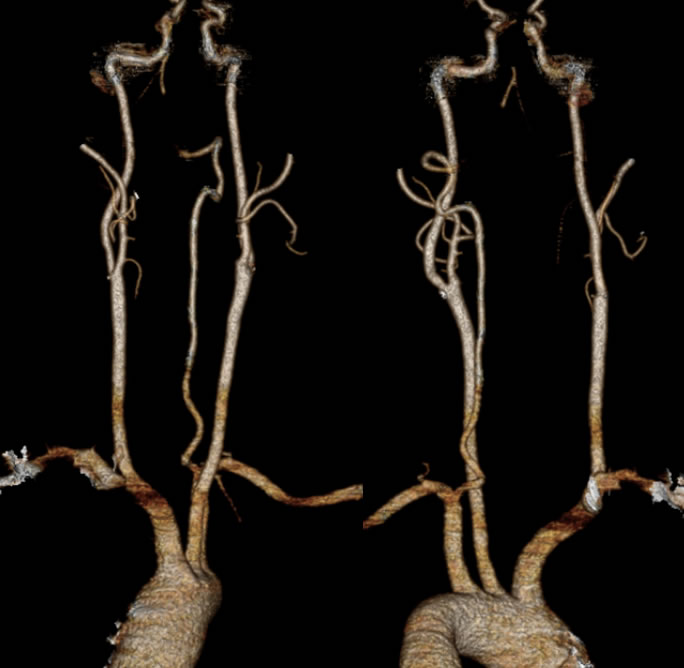
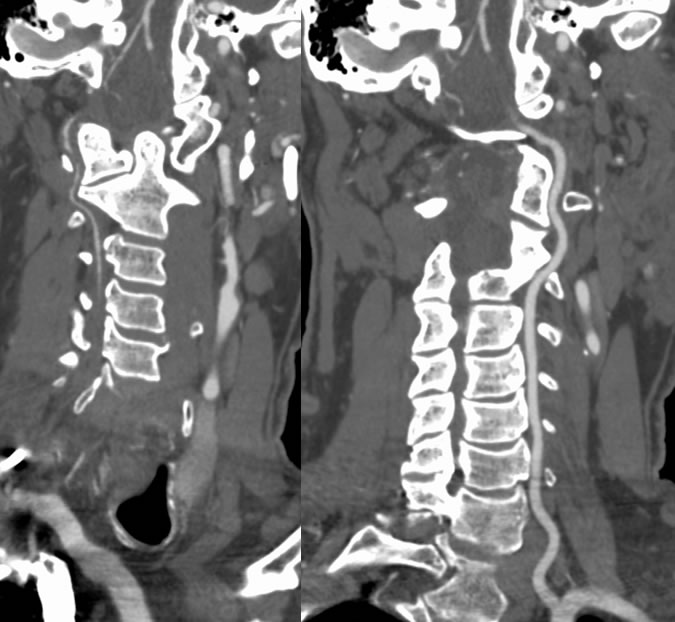
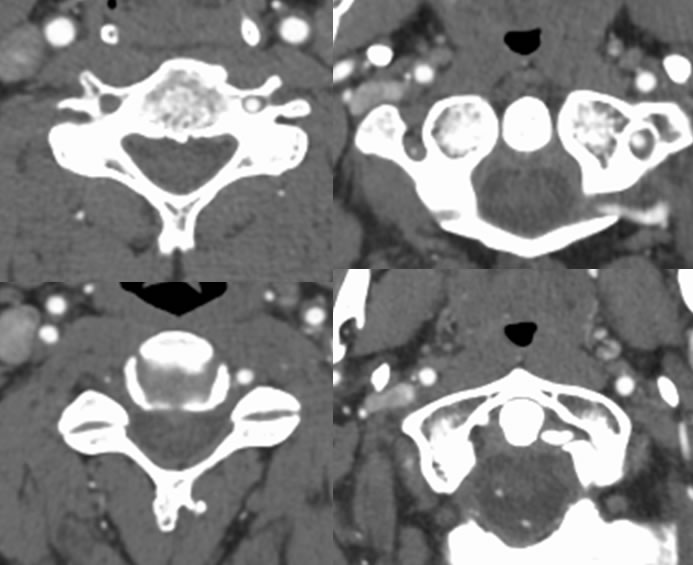
Multiple CTA images demonstrate occlusion of the dominant left vertebral artery near foramen magnum level. The right vertebral artery is hypoplastic and is occluded proximally, with minimal spotty reconstitution distally through collaterals.
Discussion:
Vertebral artery dissection may be seen in the setting of trauma, with or without cervical spine fracture. Fractures that extend through the transverse foramina are more likely to cause vertebral artery injury. Occasionally, vertebral artery dissection may occur with trivial trauma, including chiropractic neck manipulation.