Carotid cavernous fistula, direct
Findings:
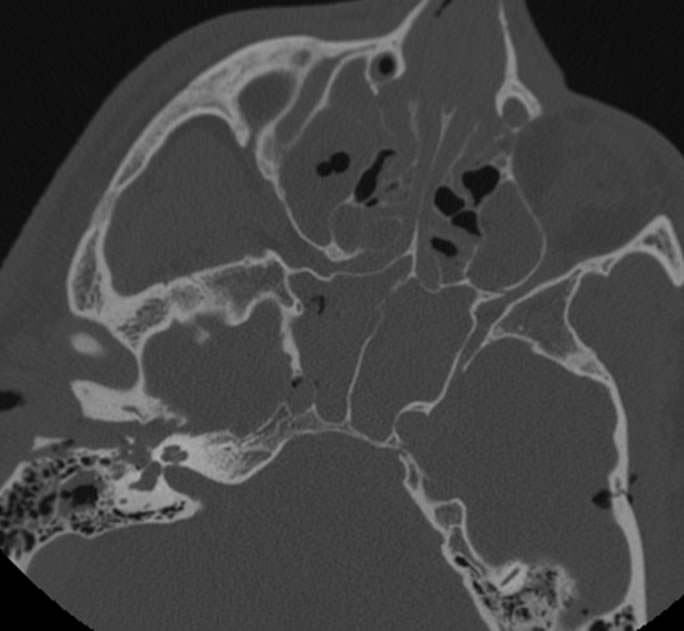
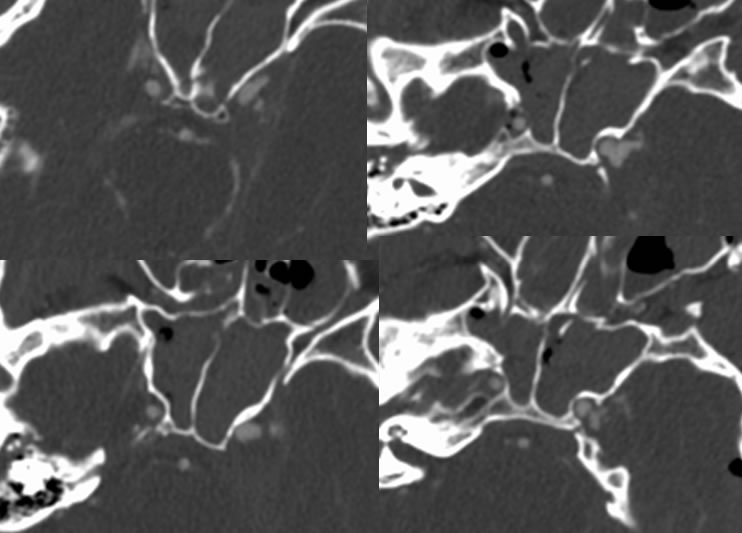
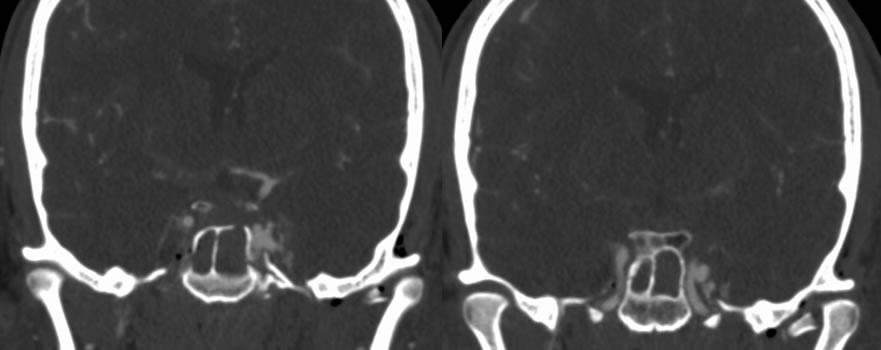
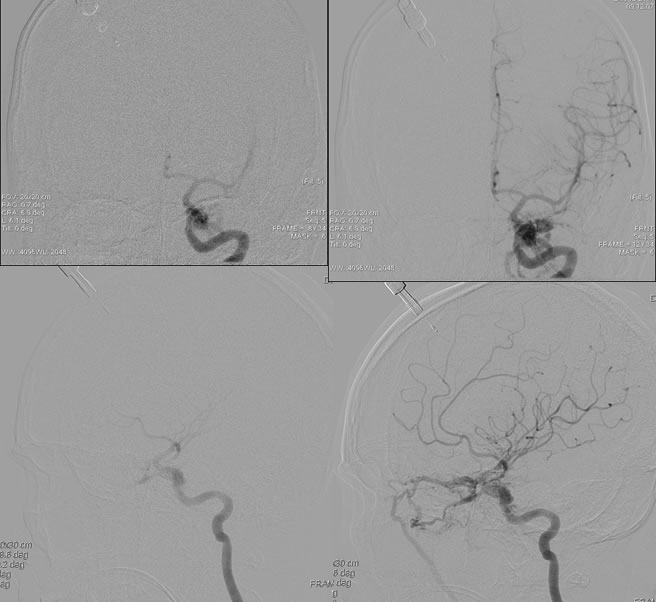
Axial skull base CT demonstrates multiple fractures involving the right temporal bone, left squamous temporal bone, bilateral carotid canals, and maxillary sinuses. There is gas within the right carotid canal. Pneumocephalus and paranasal sinus/mastoid opacification is present. Multiple CTA images demonstrate irregular contour of the left cavernous internal carotid with a multilobulated lateral projection. Selective left ICA injection demonstrates robust AV shunting arising from the left cavernous internal carotid with early venous drainage into the cavernous sinus and ophthalmic veins.
Discussion:
nClinical
nSkull base fractures vs ruptured preexisting aneurysm
nBruit, exophthalmos, orbital edema/injection, visual loss, HA, CN palsies
nImaging
nProptosis, enlarged SOV and CS, orbital edema/EOM enlarged
nMRA/CTA- shunting
nNeed conventional angio to see site of tear and guide treatment
nDdx of SOV enlargement:
nCCF, CS thrombosis, graves disease, orbital mass
nPathology
nType A- direct ICA to CS
nTypes B-D- indirect-meningeal branches of ICA to CS.
nDue to trauma or ruptured ICA aneurysm
nProximal horizontal or vertical segment
nShunting patterns- SOV and petrosal sinuses
nReflux into cortical veinsà increased risk of SAH
nRx
nembolization
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE





