
Hemorrhagic Left Cerebellar Infarction
Findings:
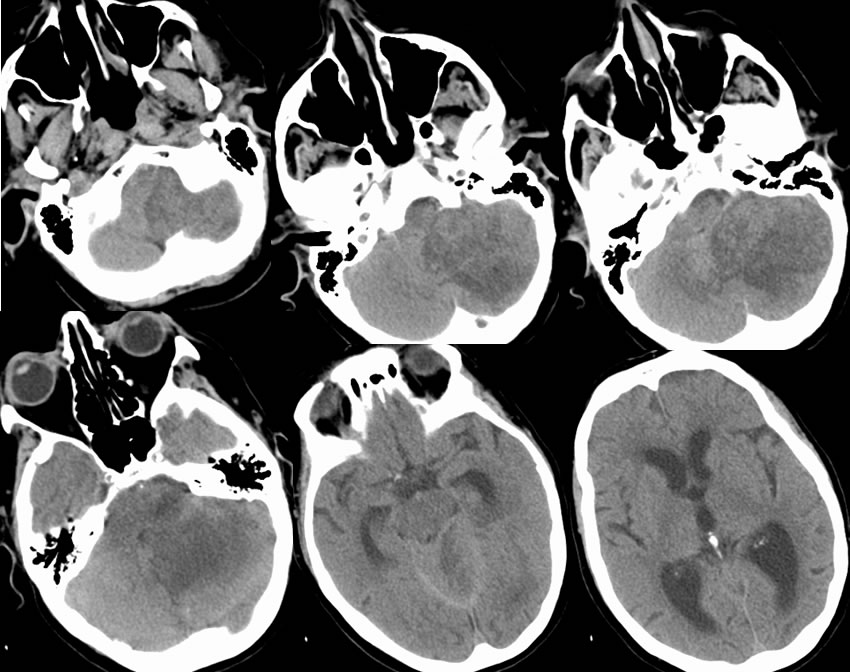
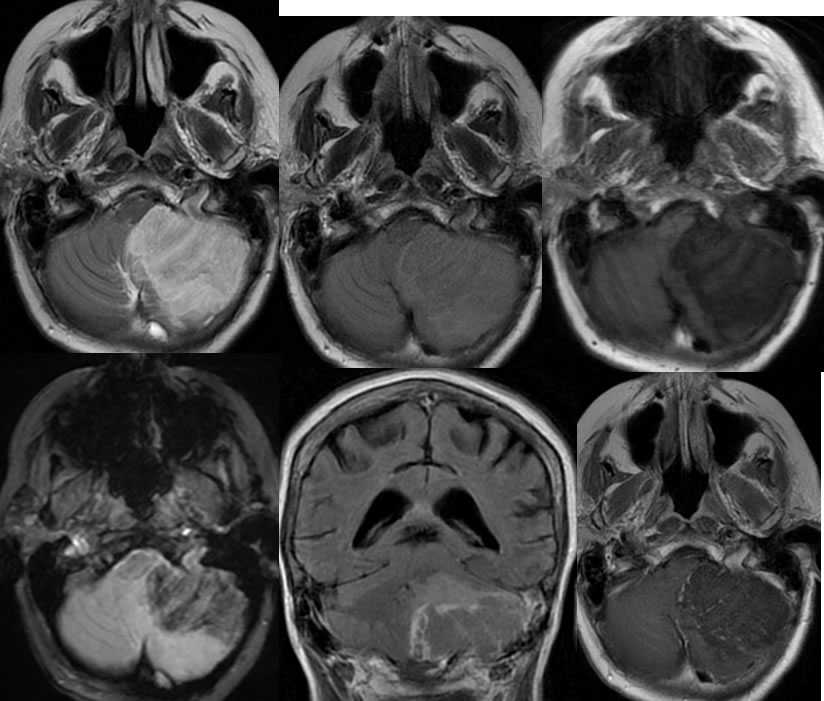
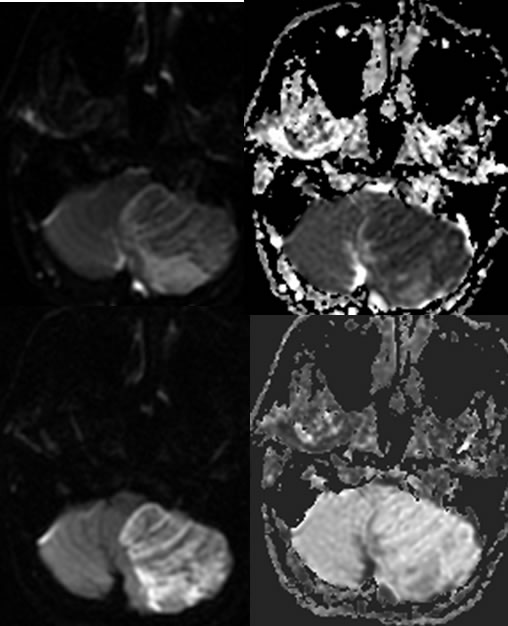
Multiple axial noncontrast CT images demonstrate heterogeneous mixed low attenuation in the inferior left cerebellum associated with significant surrounding edema and mass effect with effacement of the fourth ventricle and obstructive hydrocephalus. The MR images demonstrate a large zone of signal abnormality in the inferior left cerebellum with preserved internal architecture, spotty peripheral enhancement, and patchy zones of gradient echo hemorrhagic changes. The diffusion weighted imaging confirms restricted diffusion throughout this lesion with zones of decreased signal related to the hemorrhagic changes.
Discussion:
To the uninitiated, tumor would be suspected and was the admitting diagnosis of this patient. The presence of homogenous wedge shaped restricted diffusion with preserved architecture indicates that this represents hemorrhagic infarction. The typical patterns of enhancement and hemorrhage are also seen that substantiate infarct. The clinical neurologic deficit was also abrupt in onset. Additional discussion of stroke is found elsewhere on this site.