
Acute Bilateral MCA Distribution Infarcts
Findings:
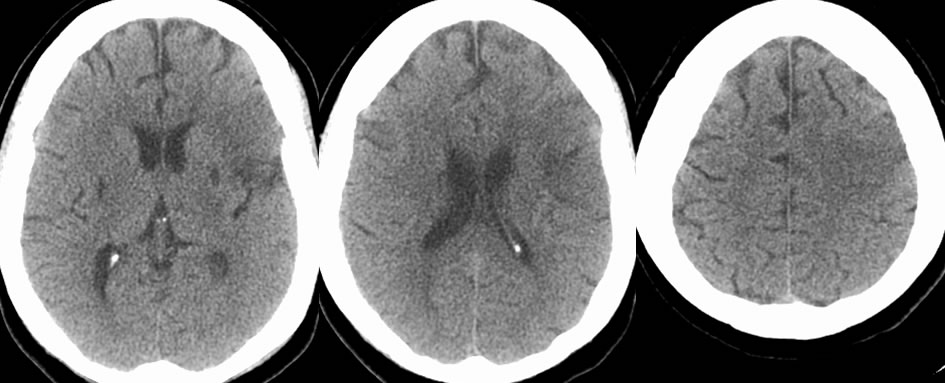
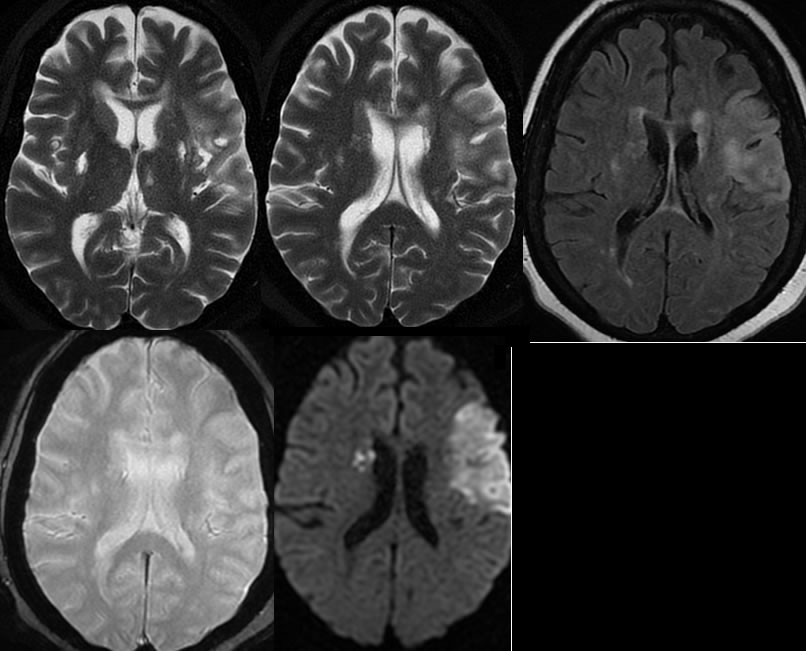
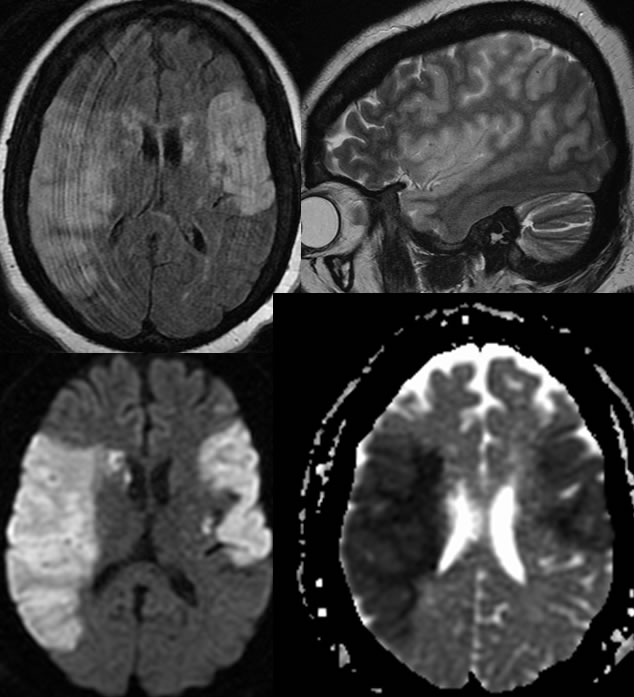
Axial CT noncontrast images demonstrate a poorly defined wedge-shaped focus of low attenuation in the left frontal lobe. More well-defined foci of low attenuation in the bilateral basal ganglia are compatible with remote lacunar infarcts. The initial MR images confirm the presence of a wedge shaped focus of diffusion restriction correlating with the low attenuation on CT, compatible with acute infarct. Other zones of acute infarction involve the right caudate nucleus. The MR again demonstrates remote infarcts in the bilateral basal ganglia and also show a remote lacunar infarct in the left thalamus. On short-term follow-up MR within 2 days while still in the hospital, an additional large zone of restricted diffusion has developed in the right frontal parietal region along the distribution of the right middle cerebral artery.
Discussion:
The exact cause of multiple infarcts in this patient has not been established definitively, but the patient does have a long standing history of drug abuse including cocaine. Additional discussion of stroke is found elsewhere on this site.