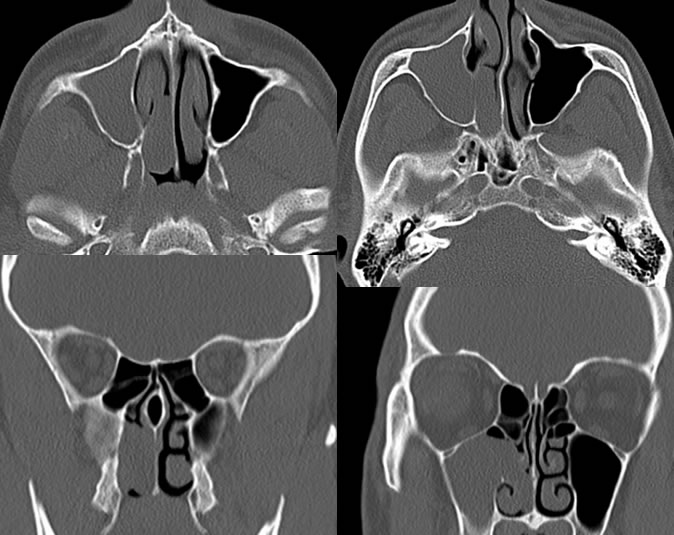

Findings:
The right maxillary sinus is completely opacified. The right maxillary ostium is widened with a lobulated lesion extending into the right nasal cavity causing subtotal opacification of the nasal cavity. The suspected choanal component of polyp measures 3.1 x 1.2 x 2.2 cm. The right maxillary sinus does not appear significantly expansile and there is no significant wall thickening. No periantral fat plane infiltration is seen. No destructive process is visible.
Differential Diagnosis:
Antrochoanal polyp, inverting papilloma, minor salivary gland neoplasm, chronic sinus disease.
Discussion:
Antrochoanal polyps are inflammatory lesions that cause obstruction of the maxillary sinus ostium with postobstructive sinus opacification. They are well defined and do not typically cause significant sinus expansion. They follow the signal and attenuation of simple or mildly complex fluid and do not show central enhancement after contrast.
They are most common in young adults and present with nasal obstructive symptoms. They comprise 3-6% of sinonasal polyps and 40% of patients have a history of allergies. The lesions are treated by surgical resection, but both the antral and choanal component including the stalk must be resected to minimize possibility of recurrence.