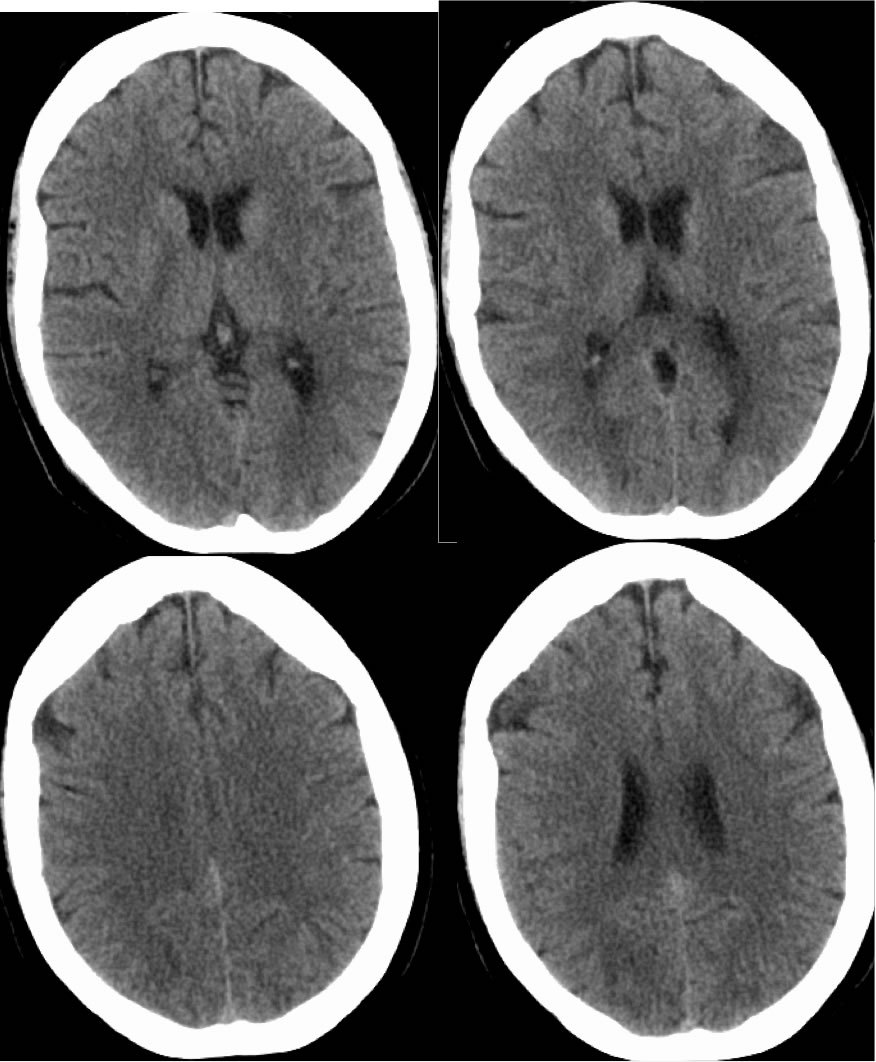
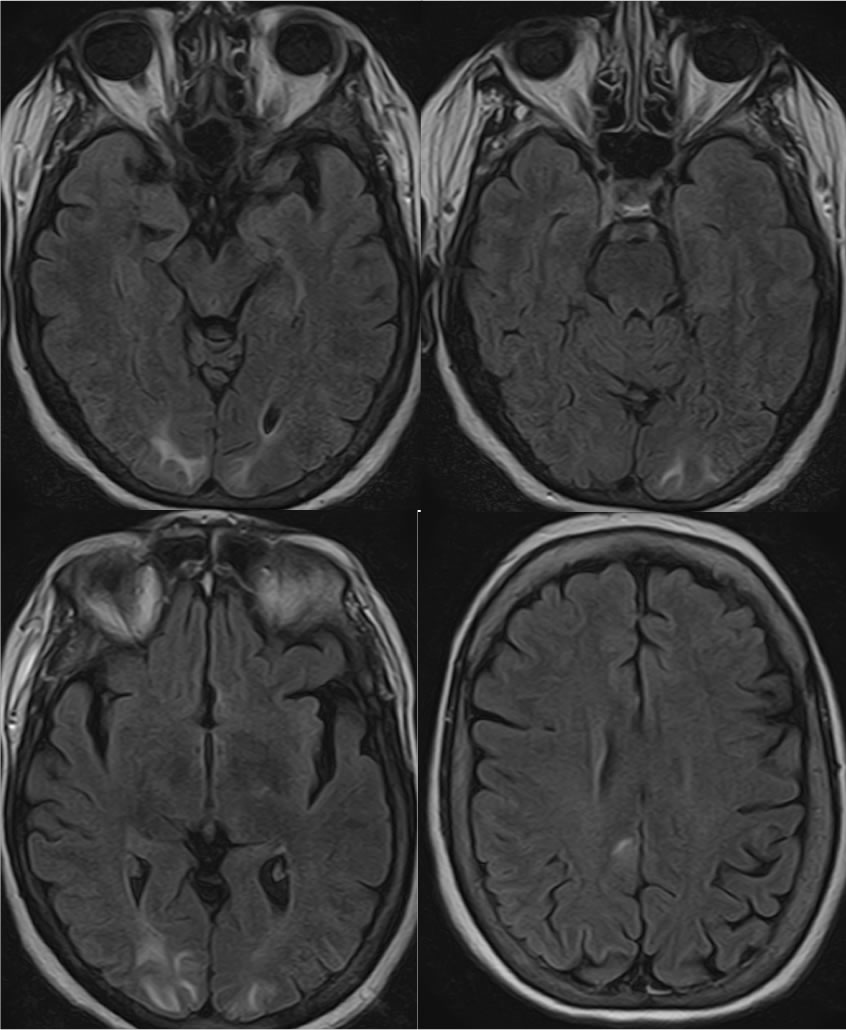
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome
Findings:
CT images demonstrate subtle nearly symmetric patchy low attenuation within the bilateral parietal occipital regions, which correlate with zones of hyperintensity on MRI FLAIR images.
Discussion:
Viewing CT images with very narrow window contrast levels are helpful to detect subtle areas of decreased attenuation which may suggest the presence of acute infarction or edema. In this case, the patchy signal abnormalities are symmetric and in a posterior distribution, fairly characteristic for PRES. Multifocal infarcts or encephalitis could appear similar. Clinical history is often helpful for distinction of these possibilities. This patient presented with headaches and blurry vision but was not significantly hypertensive.
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE



