GBM Recurrence, Dural Sinus Thrombosis
Findings:
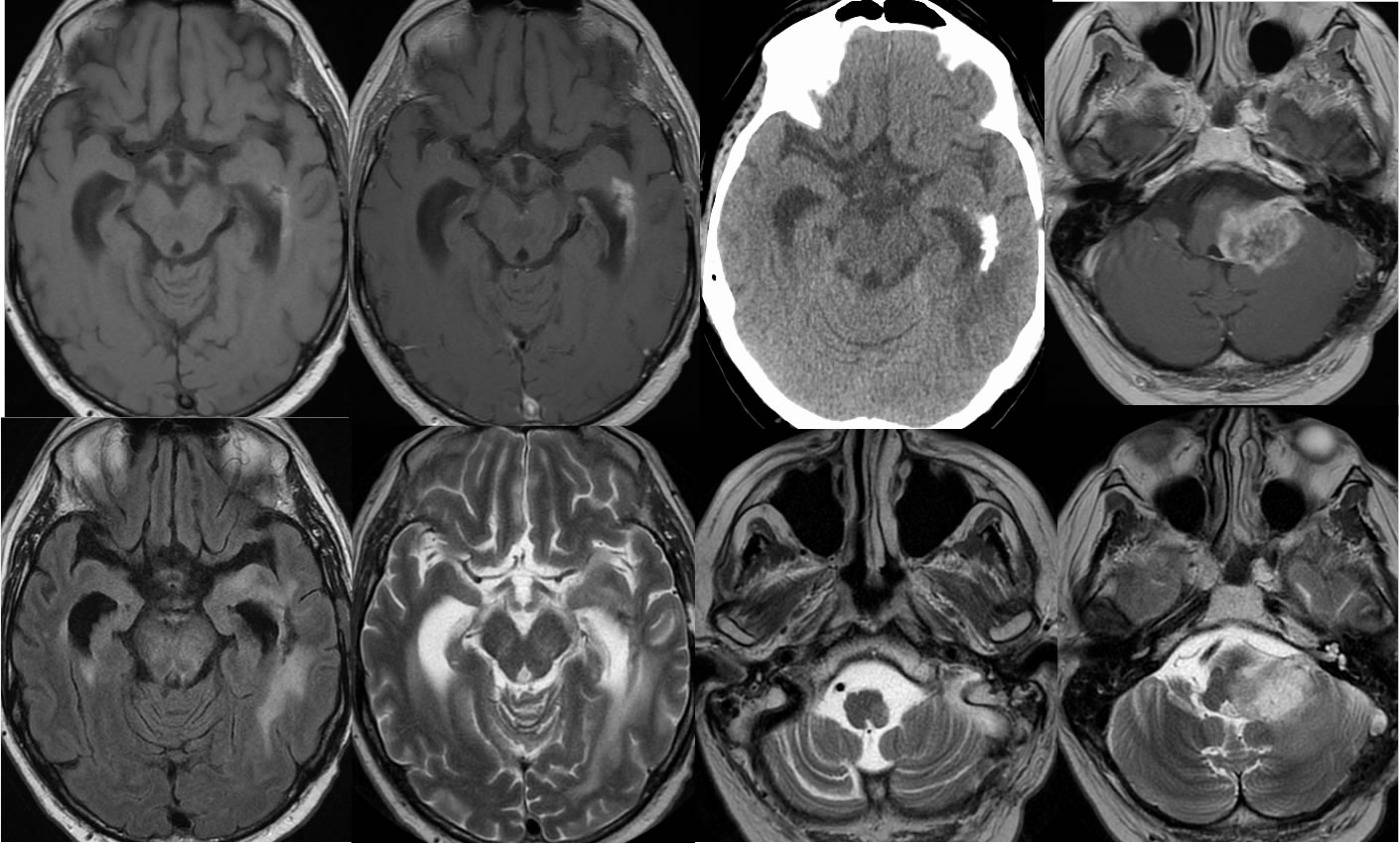
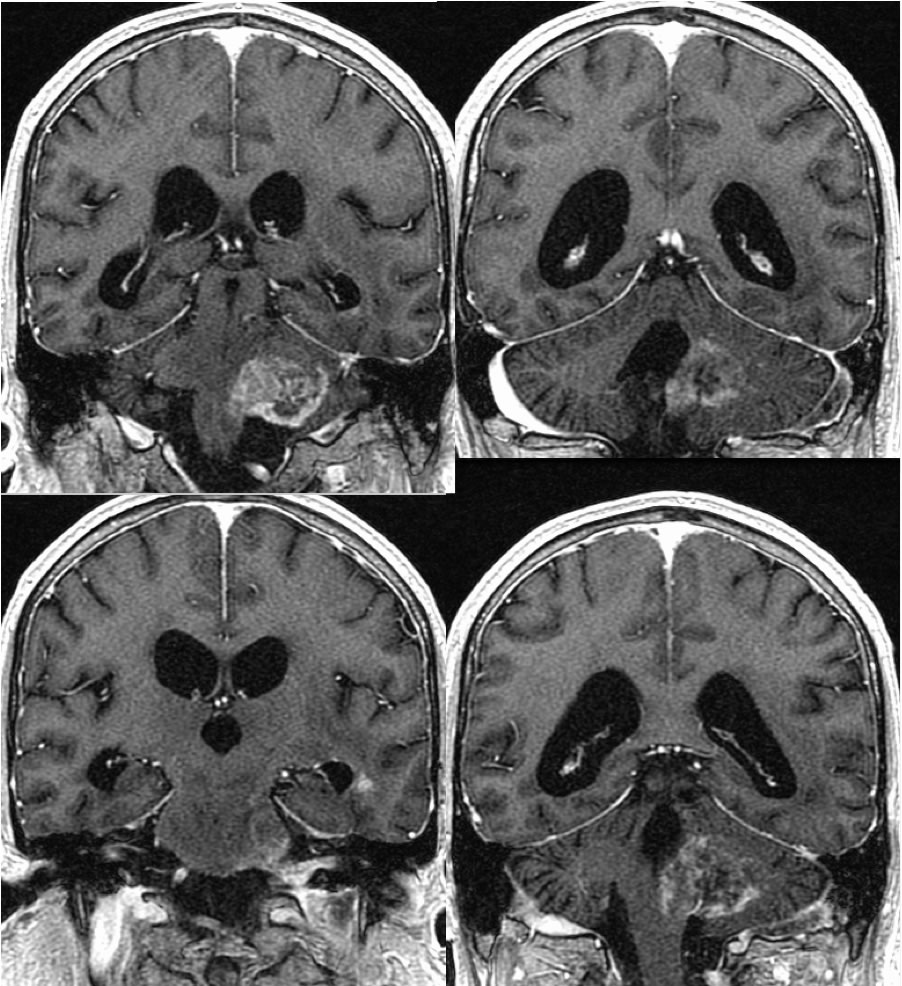
Postoperative findings of left temporal craniotomy are incompletely included. Poorly defined calcifications with superimposed enhancement are present in the left temporal periventricular region, associated with surrounding FLAIR signal alteration. A poorly defined enhancing mass involves the left medulla and middle cerebral peduncle associated with effacement of the fourth ventricular outlet foramen. There is also abnormal signal in the left transverse sinus with nonenhancing filling defect due to thrombosis. Subtle subependymal nodular enhancement is seen along the left temporal horn on coronal imaging. Additional subtle subarachnoid enhancement is present within the interpeduncular cistern and coating the brainstem.
Differential Diagnosis:
The mass within the left CP angle at first glance simulates schwannoma, but has an irregular interface with adjacent structures and is infiltrating rather than well-defined. The mass does extend exophytically into the adjacent cistern. The findings of previously treated neoplasm are also seen in the left temporal lobe. The dural sinus thrombosis is another important finding that might be easy to overlook with the distracting abnormalities in other regions. This case shows the importance of maintaining a search pattern to detect additional abnormalities after the primary obvious lesion has been discussed. The exophytic nature of this lesion extending into the cistern also should cause a dedicated search for other foci of CSF dissemination.
Discussion:
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE



