Basilar Artery Thrombosis
Findings:
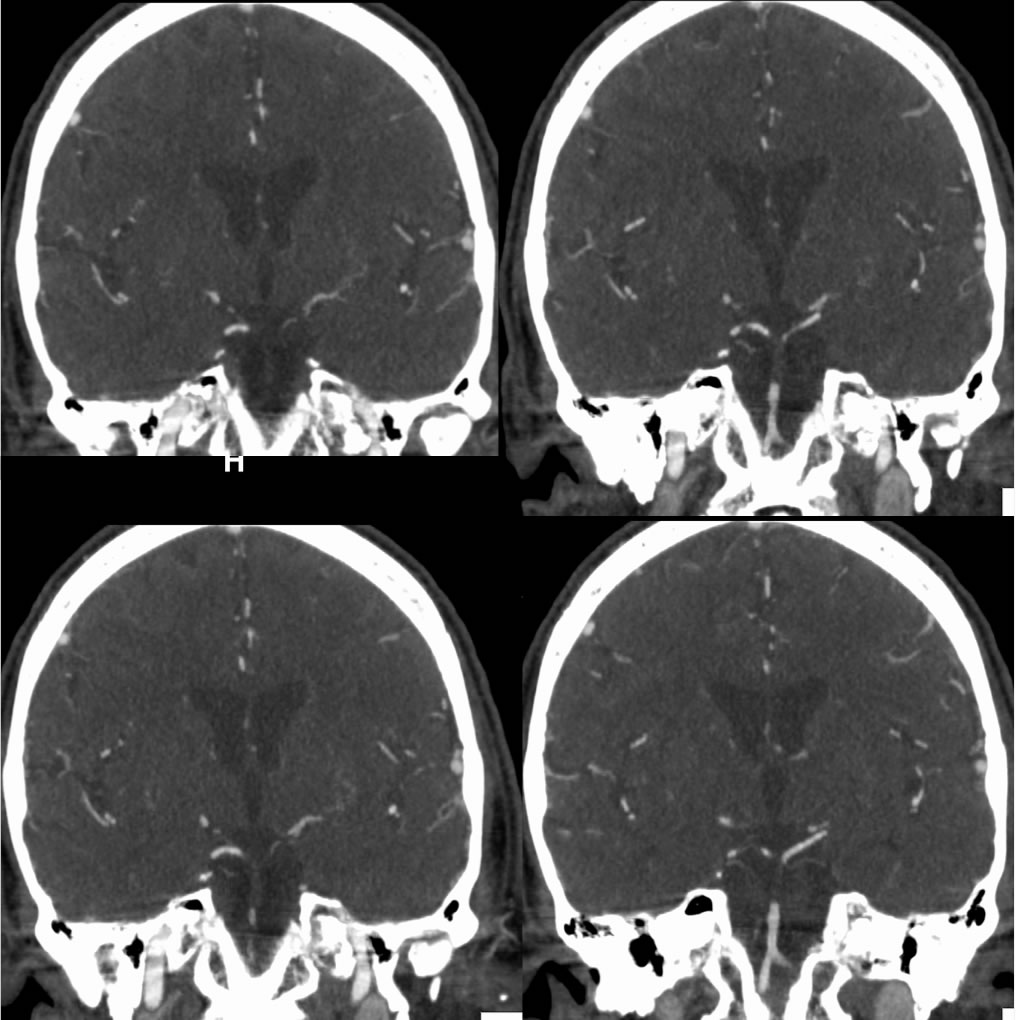
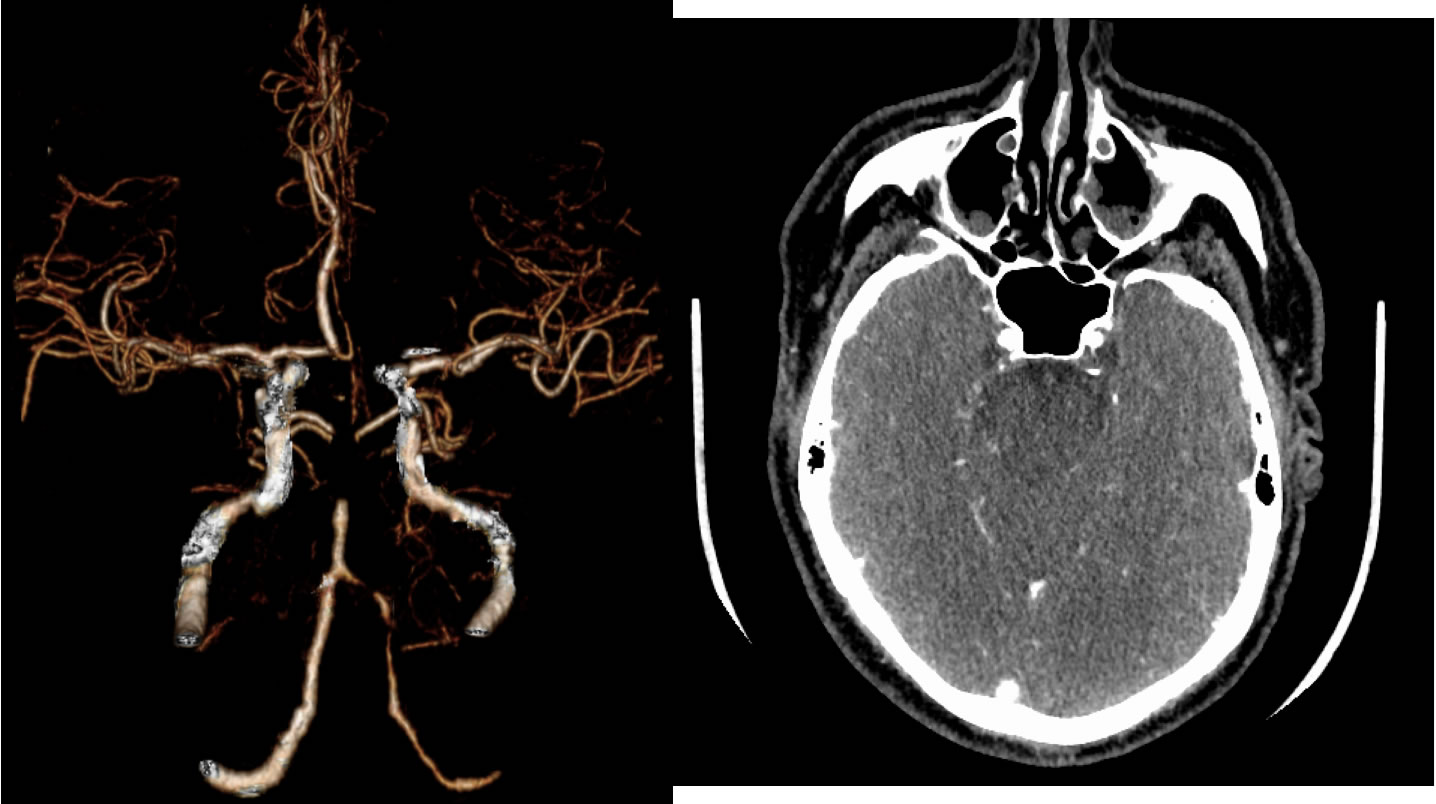
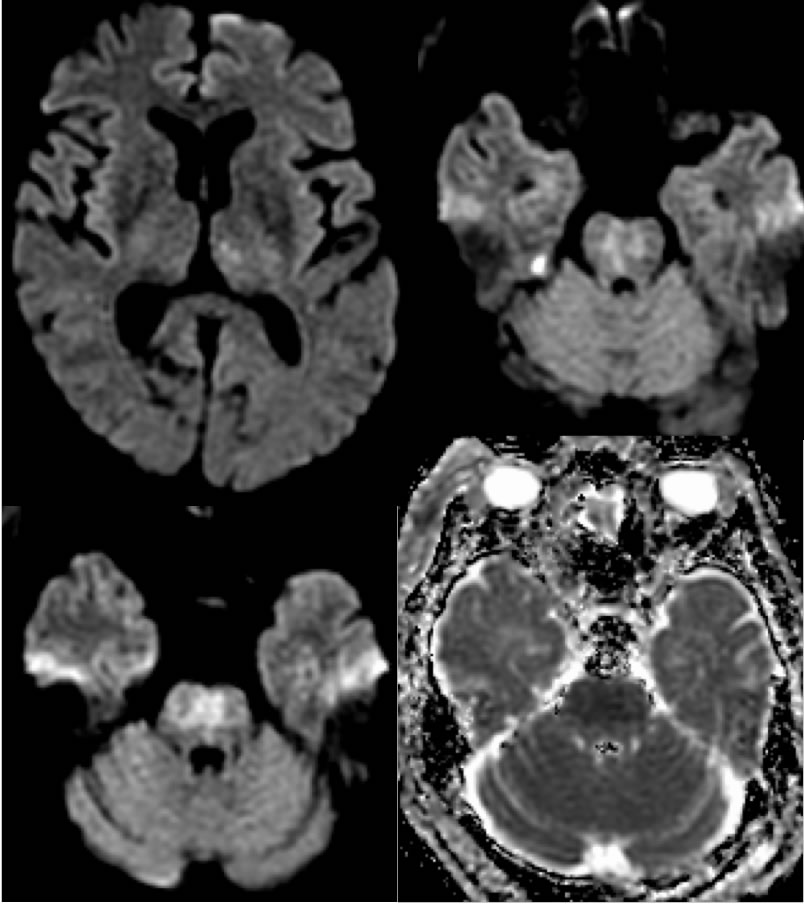
CTA images demonstrate a large occlusive thrombus within the mid through distal basilar artery. Diffusion weighted imaging demonstrates patchy restricted diffusion in the pons and left medial thalamus due to acute infarction. VRT additionally shows irregular multifocal stenosis of the left vertebral artery V4 segment.
Discussion:
Stroke is the 5th leading cause of adult death and disability with over $72 billion in healthcare costs. Up to 90% of strokes are ischemic as opposed to hemorrhagic. Large vessel infarctions may be embolic or less commonly in situ with underlying atherosclerotic disease. Large vessel emboli may be cardiogenic most commonly due to atrial fibrillation, arise from ulcerated atherosclerotic disease of proximal cervical vessels, or occasionally may be venous thrombi crossing a patent foramen ovale. Other cardiac disease such as valvular disease, cardiomyopathy, or MI also pose cardioembolic risk. 20% of acute strokes are cardioembolic in origin and have the highest 1 month mortality.
An important point in this case is the presence of hyperacute restricted diffusion which should not be confused with subacute infarction. The DWI hyperintensity is not "light bulb" bright, but there is very dark signal on the ADC map indicating acute to hyperacute infarction.
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE




