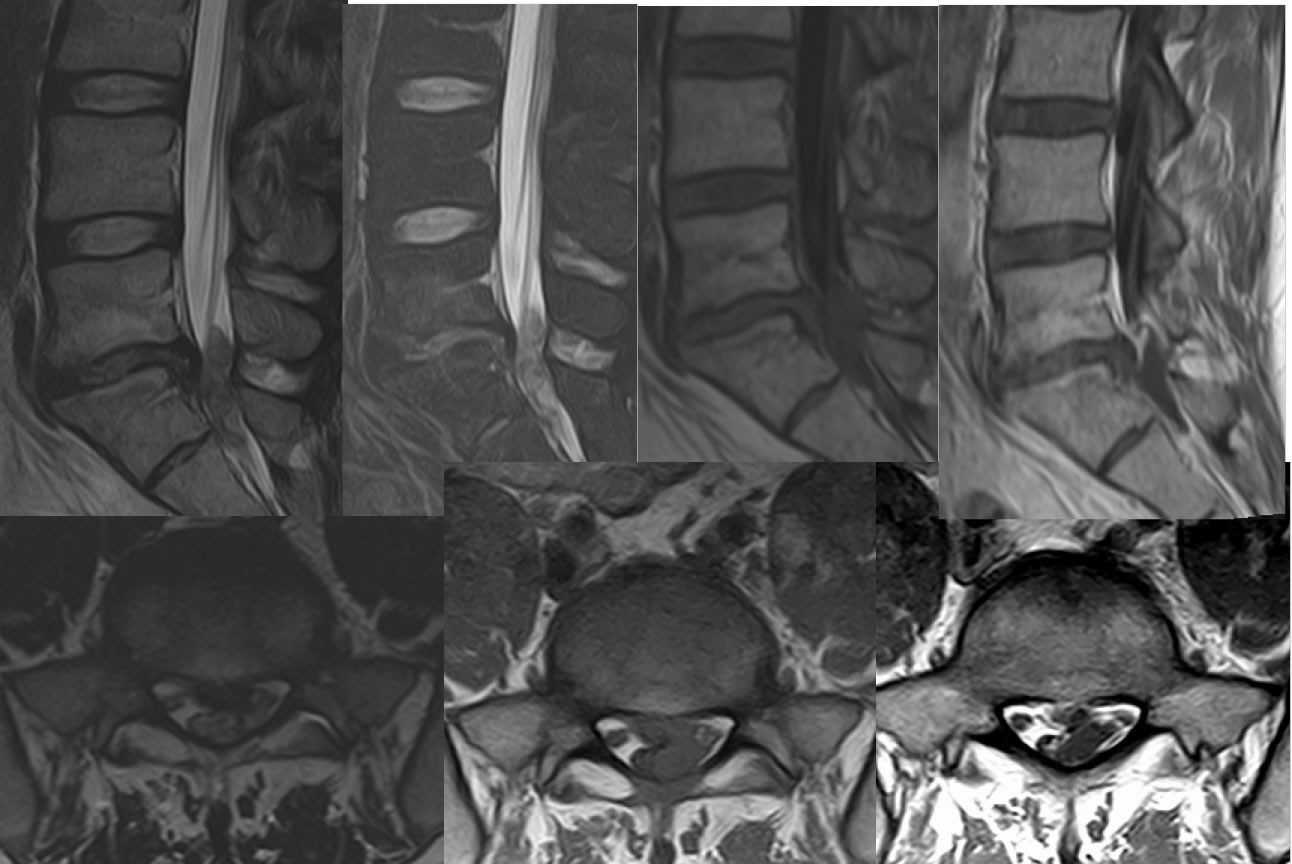
Lumbar Disc Extrusion, Posterior Epidural
Findings:
Sagittal T2, sagittal fat saturated T2, sagittal T1, and sagittal T1 post contrast images demonstrate disc space narrowing and slight retrolisthesis at L5-S1 associated with discogenic fatty endplate conversion. A large irregular focus of hypointensity on T2 weighted images is located posterior to the thecal sac at L5-S1 causing significant thecal sac compression. Axial images demonstrate contiguity of the dorsal epidural lesion with the disc margin, extending along the left lateral aspect of the thecal sac into the dorsal epidural space causing significant thecal sac compression.
Discussion/Differential Diagnosis:
The contiguity of this lesion with the disc annulus and isointensity to nucleus pulposis makes anything other than a disc extrusion very unlikely for this epidural lesion. Epidural masses overall have a broad differential diagnosis including neoplasm and infectious process. As opposed to posterior disc protrusion/extrusion, the posterolateral epidural extrusion is very rare. No differentiating pathogenesis has been elucidated.
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE
