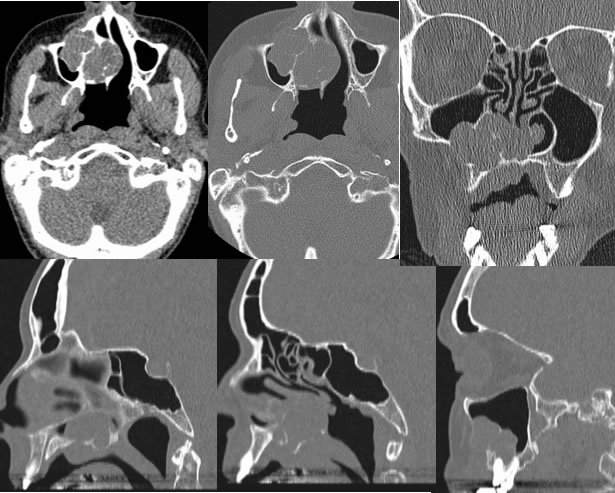
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Findings:
Axial, coronal , and sagittal CT images, most with bone reconstructions, demonstrate an expansile mass with bone destruction involving the right maxilla and hard palate. There is associated bone remodeling due to a long-standing process. The mass demonstrates soft tissue attenuation. The mass extends into the nasal cavity and the right maxillary sinus.
Discussion/Differential Diagnosis:
A soft tissue mass involving the hard palate has a broad differential diagnosis, including primary squamous cell carcinoma, metastasis, minor salivary gland tumor, or a primary bone lesion such as fibrous dysplasia. The appearance is not definitive for salivary gland tumor, but should be considered due to the bone remodeling indicating a long standing slowly growing process. Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) involving the hard palate is a rare presentation and is a slowly growing submucosal mass as opposed to more aggressive growth seen with the more common malignant tumors such as mucoepidermoid carcinoma that arise from minor salivary glands. PA is the most common salivary gland neoplasm and is most common in the parotid gland. Risk of malignancy is inversely proportional to the size of the gland, with up to 80% of parotid tumors being benign.
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE
