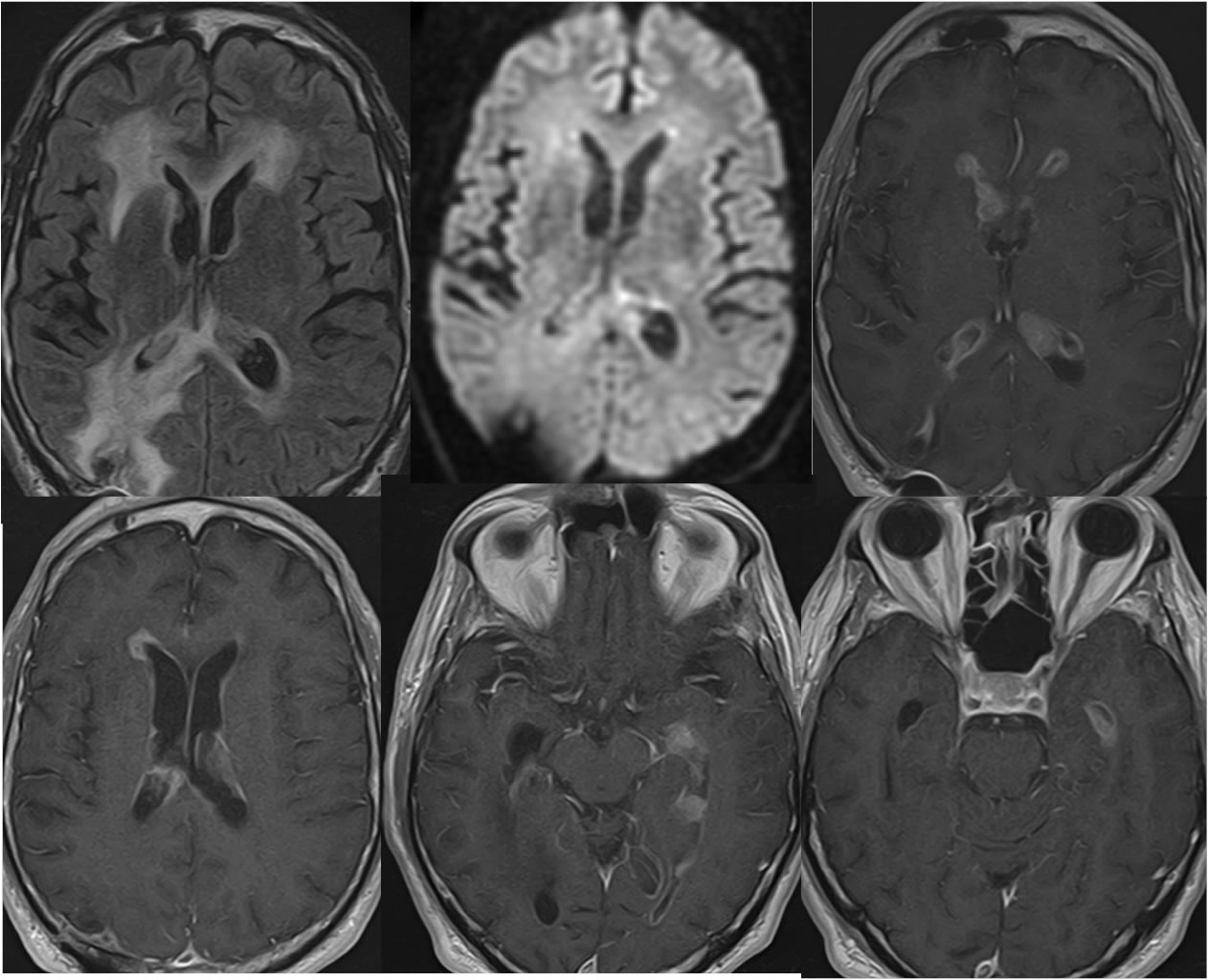
Metastatic Melanoma with Intraventricular Dissemination
Findings:
Axial FLAIR, single DWI image, and four axial T-1 post contrast images demonstrate multiple enhancing intraventricular masses including subependymal linear nodular enhancement. A superimposed postoperative site is present in the right parietal lobe with associated enhancement. There is extensive periventricular and right parietooccipital FLAIR signal alteration. No diffusion restriction is seen.
Discussion/Differential Diagnosis:
The differential diagnosis of intraventricular enhancing lesions includes metastatic or less likely primary neoplasm with intraventricular dissemination. Infectious process with subependymal enhancement may be seen in the setting of ventriculitis, but the nodular enhancement would not be expected. Intraventricular metastases are rare, most commonly seen with lung, renal cell, melanoma, and breast primary neoplasm. Melanoma involving the CNS is almost always metastatic, but may rarely arise as a primary from leptomeningeal melanocytes. The imaging features are of cellular and/or hemorrhagic lesions, hyperdense on CT, intermediate cellular signal on T2, and T1 precontrast hyperintensity due to melanin and/or hemorrhage.
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE

