PML IRIS
Findings:
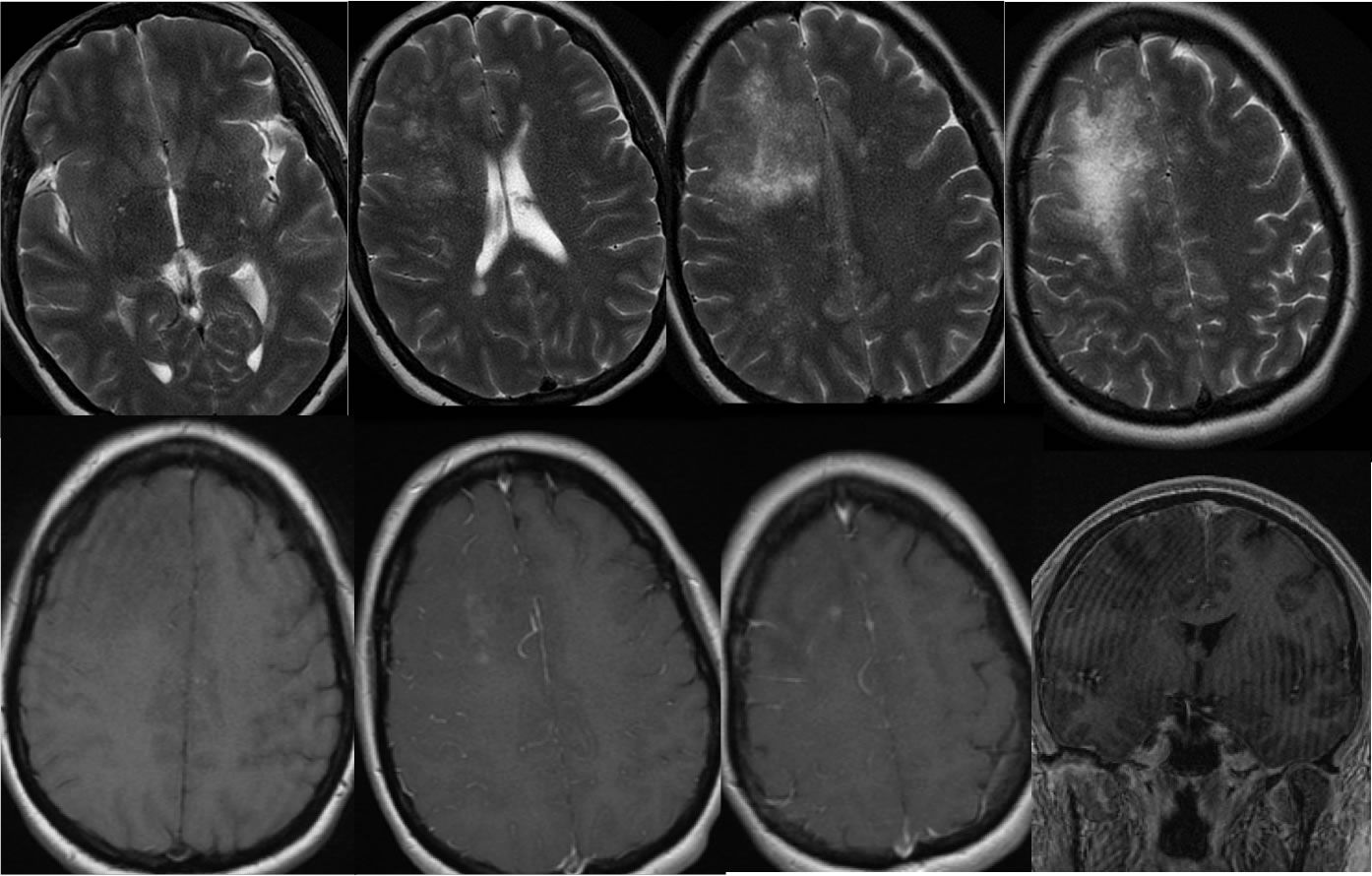
Four axial T2 weighted images demonstrate a confluent irregular zone of signal abnormality in the right frontal white matter associated with mild mass effect. The T2 signal abnormality has a granular appearance. Superimposed ovoid white matter lesions related to multiple sclerosis are present. Axial T1 pre-and post contrast images and coronal T1 postcontrast demonstrate several spotty and patchy zones of abnormal enhancement within the right frontal lobe process.
Discussion/Differential Diagnosis:
The differential diagnosis for this process includes IRIS in the setting of MS treatment, active tumefactive demyelination, development of superimposed glial neoplasm, or superimposed encephalitis. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) is defined as a clinical worsening that coincides with immune recovery, seen in HIV patients treated with HAART, or other patients including but not limited to those with MS that have undergone immunomodulating therapy. Some MS patients that are treated with immunomodulators including natalizumab and have seropositivity for JC virus may develop an aggressive form of PML. The s subtype is simultaneous PML and IRIS, and the d subtype is PML that worsens with immune recovery. While there is some overlap in imaging appearance, the presence of mass effect, granular appearance, and patchy enhancement not limited to the leading edge should help distiguish PML-IRIS from tumefactive demyelination. The development of confluent zones of signal abnormality that are atypical in appearance for demyelination, not ovoid periventricular, should raise suspicion for PML-IRIS. The process typically improves after cessation of the offending agent. Companion cases of PML and tumefactive demyelination:
-progressive
multifocal leukoencephalopathy
-progressive
multifocal leukoencephalopathy 2
-progressive
multifocal leukoencephalopathy 3
-Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
-tumefactive demyelination
-tumefactive demyelination 2
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE

