B cell lymphoma
Findings:
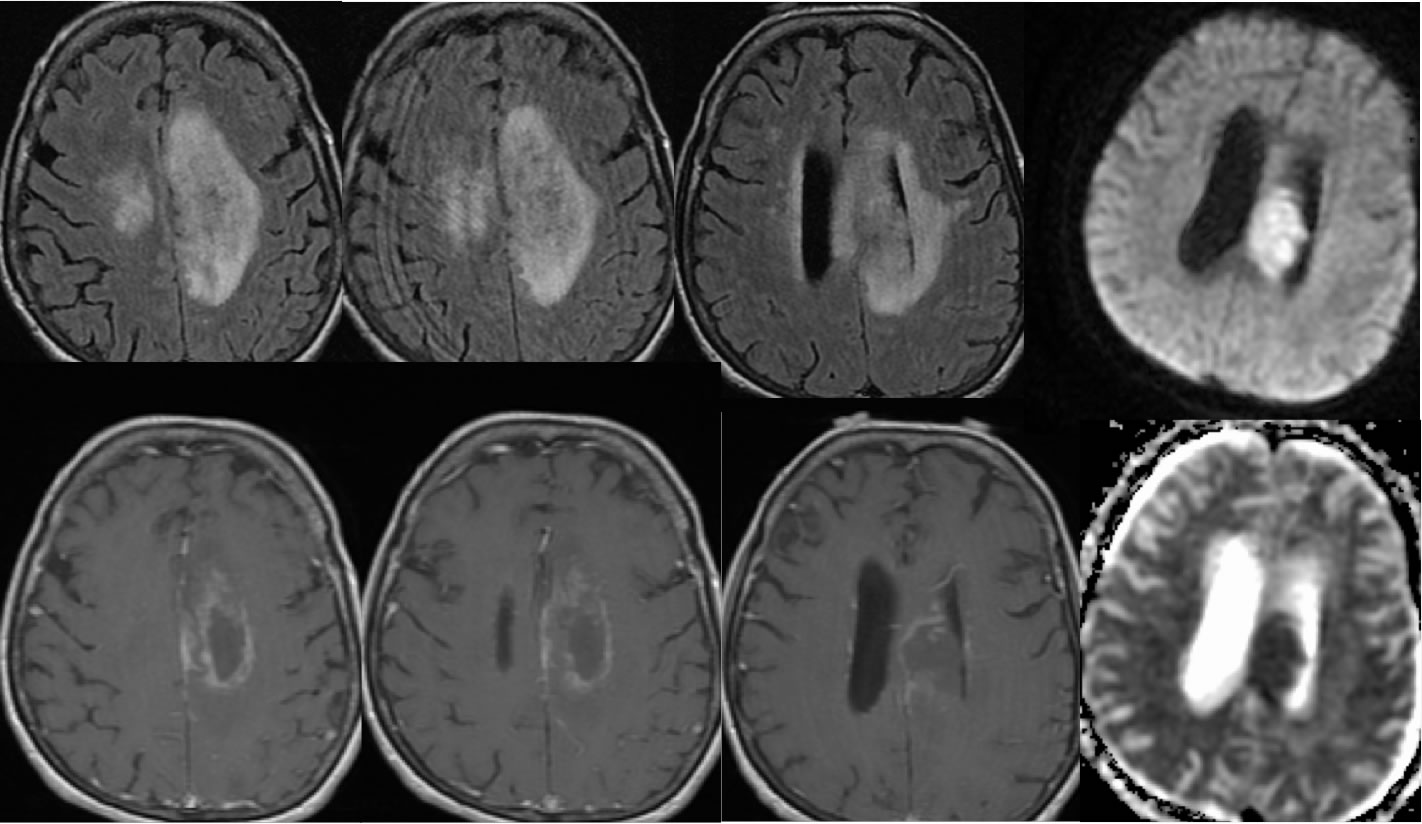
Axial FLAIR, axial T1 post contrast, and diffusion ADC images demonstrate a poorly defined peripherally enhancing infiltrative mass involving the left body of the corpus callosum and centrum semiovale extending into the corona radiata. The central portion of the mass demonstrates prominent restricted diffusion. The surrounding enhancement is very poorly defined without a well-defined wall surrounding the focus of restricted diffusion, and there is superimposed leptomeningeal enhancement in the parasagittal region. Mild mass effect is present. The infiltrative FLAIR signal alteration crosses midline into the centrum semiovale and there is superimposed minimal white matter disease likely due to chronic microvascular ischemia. Scattered zones of patchy hypointensity are also present within the lesion on the FLAIR images.
Discussion/Differential Diagnosis:
The differential diagnosis for this process includes neoplastic disease either primary or metastatic, encephalitis, tumefactive demyelination, evolving abscess, or subacute infarct much less likely. Involvement of the corpus callosum with mass effect should indicate that neoplasm is more likely than a demyelinating process. Unusual features of this lesion include central restricted diffusion in the absence of central enhancement and poorly defined rather than nodular enhancement, but the lack of prominent central enhancement is a feature sometimes seen with B cell lymphoma. Additional cases and discussion of CNS lymphoma:
-lymphoma1
-lymphoma2
-lymphoma3
-lymphoma4
-lymphoma5
-lymphoma6
-lymphoma6 intraventricular
BACK TO
MAIN PAGE

